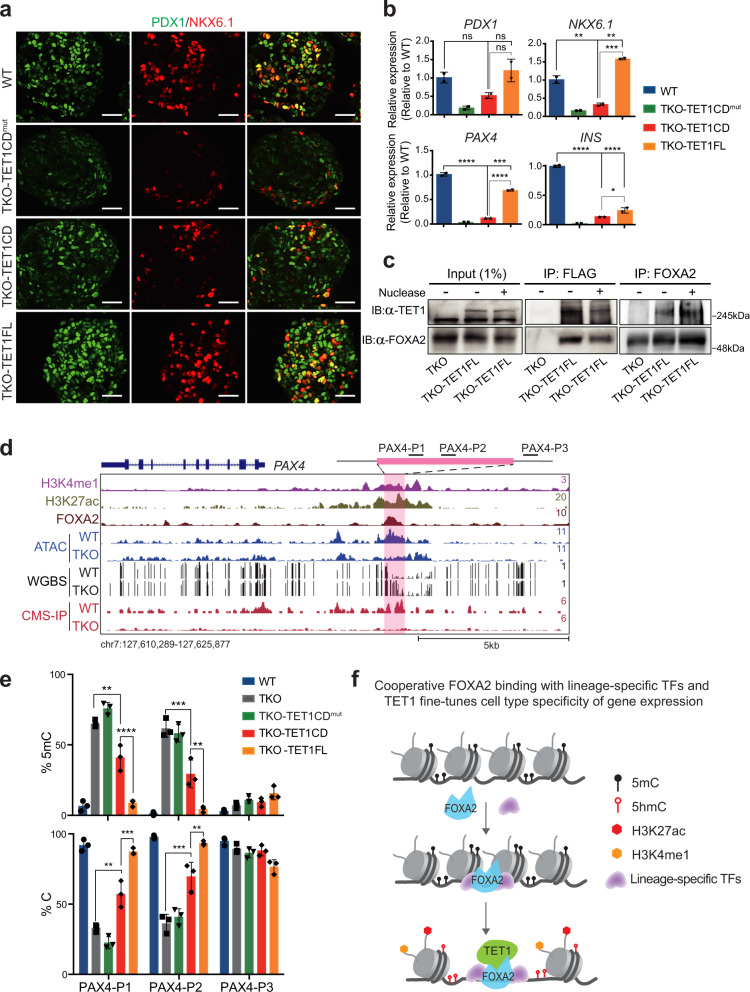
Fig. 6. Full-length TET1 is required for the establishment of a hypomethylated PAX4 enhancer.
a Immunostaining of PDX1 and NKX6.1 at the PP stage for WT, TKO-TET1CDmut, TKO-TET1CD, and TKO-TET1FL cells (n = 3 independent differentiations; scale bar = 50 μm). b Expression of PDX1, NKX6.1, PAX4, and INS in WT, WT, TKO-TET1CDmut, TKO-TET1CD, and TKO-TET1FL cells at the PE stage (n = 2 independent differentiations; p = 0.001, p = 0.0021, p = 0.0001, p = 7.4 × 10−7, p = 0.0002, p = 3.4 × 10−5, p = 1.8 × 10−5, p = 3.7 × 10−5, and p = 0.0498 for WT versus TKO-TET1CD, WT versus TKO-TET1FL, and TKO-TET1CD versus TKO-TET1FL of relative expression for NKX6.1, PAX4, and INS, respectively; one-way ANOVA with Turkey’s multiple comparison test). All bar graphs show mean ± SD. c Immunoprecipitation of ectopic TET1 or endogenous FOXA2 in TKO-TET1FL cells. Cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG or anti-FOXA2 antibodies, followed by immunoblotting of TET1 or FOXA2. Nuclease treatment on TET1-FOXA2 interaction is indicated. TKO is included as a control (n = 3 independent experiments). d Genome-browser view of the PAX4 locus with increased methylation and decreased chromatin accessibility upon TET depletion at a FOXA2-bound site featured enhancer signatures H3K4me1 and H3K27ac. e Locus-specific increase in 5mC at the PAX4 enhancer in TKO or TKO-TET1CD samples compared with WT and TKO-TET1FL samples. Percentages of unmethylated cytosine and 5mC at CCGG sites are shown (n = 3 independent differentiations; p = 0.0011, p = 9.1 × 10−5, p = 0.0005, p = 0.0033, p = 0.0014, p = 0.0003, p = 0.0004, and p = 0.0055 for TKO versus TKO-TET1CD and TKO-TET1CD versus TKO-TET1FL of percentages of 5mC and unmethylated cytosine at PAX4-P1 and PXA4-P2 loci, respectively; one-way ANOVA with Turkey’s multiple comparison test). All bar graphs show mean ± SD. f Schematic model depicting cooperative FOXA2 recruitment with lineage-specific TFs and TETs. Lineage-specific TFs, such as PTF1A and NEUROD1, stabilize the binding of FOXA2 which enables the recruitment of TET1 to induce DNA demethylation, chromatin opening, and fine-tuning cell type-specific gene expression.