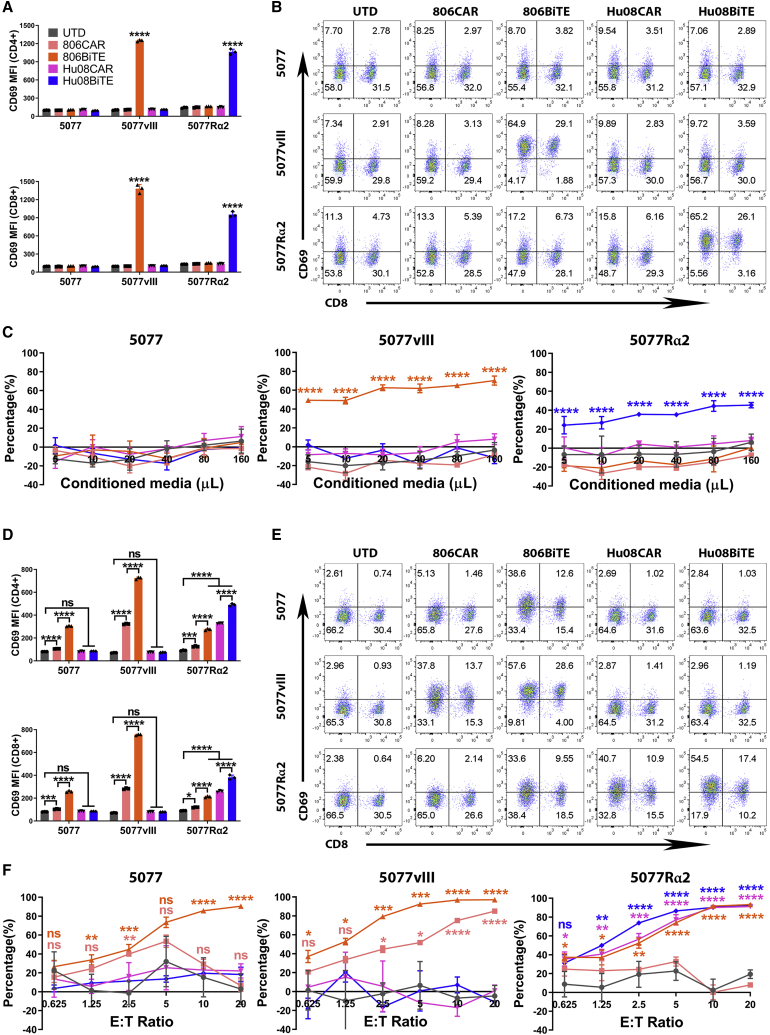
Figure 3.
BiTE T cells respond to target positive glioma cells
(A) UTD T cell activation, as demonstrated by CD69 expression, in CD4+ (top) and CD8+ (bottom) T cells after 16 h co-culture with conditioned media from CAR/BiTE T cells. (B) Flow-based results of representative samples in (A). CD8 was stained to distinguish the CD4-positive and CD8-positive subgroups of T cells along the x axis. (C) Bioluminescence cytotoxicity assay of UTD T cells co-cultured with tumor cell lines and conditioned media of CAR/BiTE T cells. (D) T cell activation, as measured by CD69 expression, in CD4+ (top) and CD8+ (bottom) T cells after 16 h co-culture of CAR/BiTE T cells with target cells. (E) Flow cytometry panels of bar graphs in (D). CD8 was stained to distinguish the CD4-positive and CD8-positive subgroups of T cells along the x axis. (F) Bioluminescence cytotoxicity assays of CAR/BiTE T cells co-cultured with tumor cell lines was analyzed at different effector/target (E:T) ratios (0.625:1, 1.25:1, 2.5:1, 5:1, 10:1, and 20:1) and compared with the UTD T cell group. Statistically significant differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test. ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation.