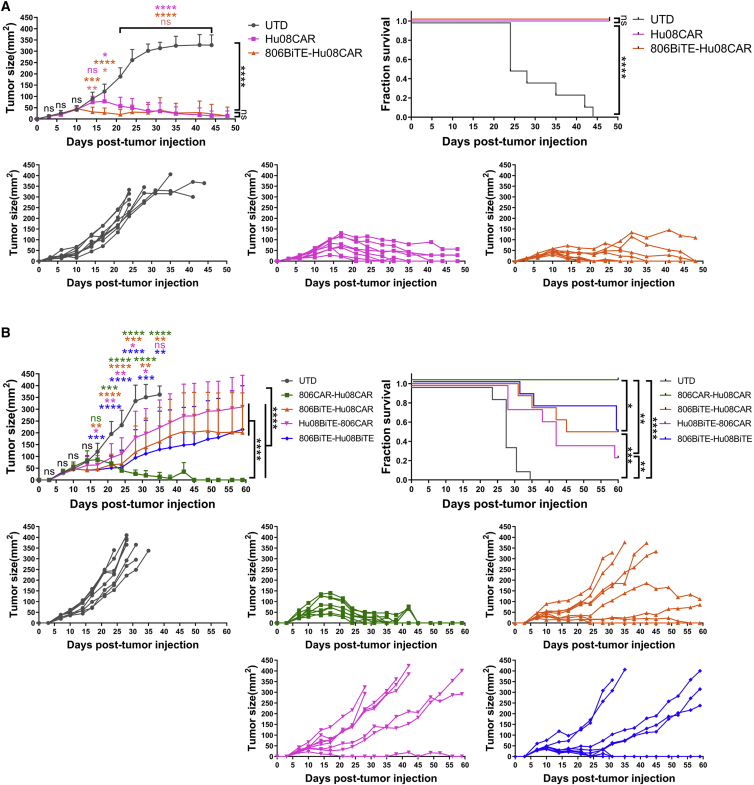
Figure 8.
BiTE transduced T cells significantly delay early tumor growth in a GBM implanted mouse model
(A) There were 800,000 Hu08CAR- and 806BiTE-Hu08CAR-positive T cells or the same number of UTD T cells that were injected intravenously (n = 8) 8 days after D270 subcutaneous implantation. (B) There were 1,200,000 bivalent targeting construct-transduced T cells (806CAR-Hu08CAR, 806BiTE-Hu08CAR, Hu08BiTE-806CAR, and 806BiTE-Hu08BiTE) or the same number of UTD T cells that were injected intravenously (n = 8) 8 days after D270 subcutaneous implantation. Tumor size was compared between each group. Statistically significant differences of tumor size at each time point were calculated by one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey test. Linear regression was used to test for significant differences between the experimental groups. Survival based on time to end point was plotted using a Kaplan-Meier curve (Prism software). Statistically significant differences were determined using log rank test. ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation.