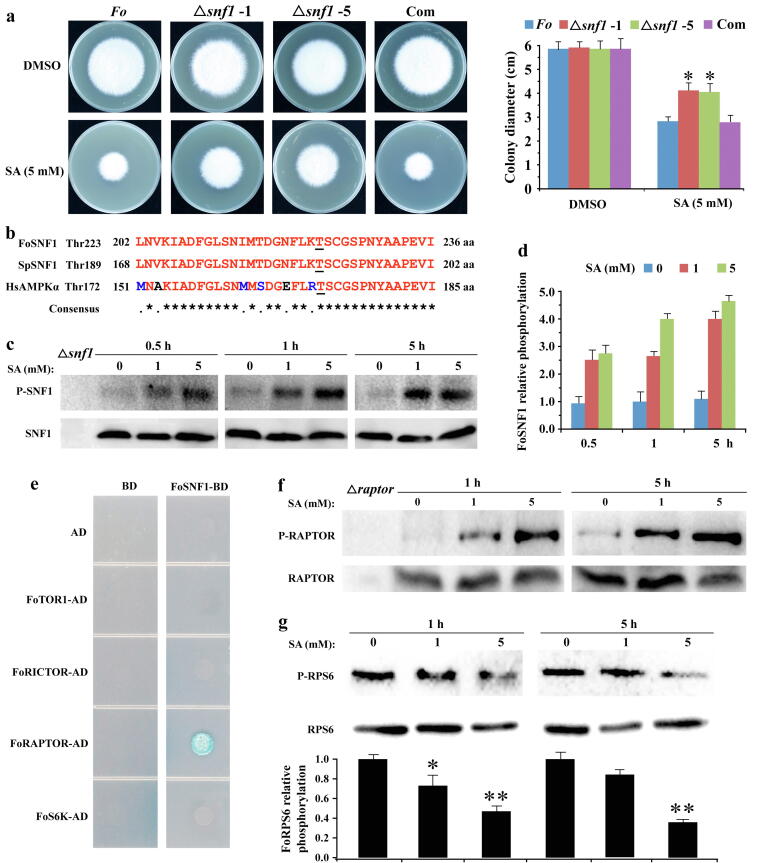
Fig. 5.
SA inhibited FoTOR signaling pathway by activating FoSNF1 in F. oxysporum. a Hyphae of Fo-4, Δsnf1, and complemented strain (Com) were incubated on PDA plates with DMSO and SA for 6 days. The data represents the mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Asterisks denote student’s t test significant difference compared with that of Fo-4 (*P < 0.05). b Sequences alignment of the conserved activation loops of FoSNF1, SpSNF1, and HsAMPKα. Phosphorylated residue of AMPKα was shown with an underline. Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Hs, Homo sapiens. c SA phosphorylated the T223 of FoSNF1 in F. oxysporum. Hyphae of Fo-4 were treated with different concentrations of SA for 0.5, 1, and 5 h. d Relative phosphorylation level of FoSNF1 in different concentrations of SA treatment. The data represents the mean ± SD of n = 2 independent experiments. e Screening the interaction proteins of FoSNF1 by yeast two-hybrid assay. The full-length CDS of FoSNF1 was inserted into BD vector; other genes were inserted into AD vector. AD: pGADT7, BD: pGBKT7. Vectors BD and AD were used as negative controls. Transformants with the AD and BD constructs were assessed for growth on synthetic medium lacking His, Leu, Ade and Trp medium at 28 °C for 3 days. f Western blot analysis of FoRAPTOR phosphorylation. Hyphae of Fo-4 were treated with different concentrations of SA for 1 and 5 h. g Western blot analysis of FoRPS6 phosphorylation. Hyphae of Fo-4 were treated with different concentrations of SA for 1 and 5 h, and the indicated bands were quantified relative to total FoRPS6 using the software Image-Pro Plus. The data represents the mean ± SD of n = 2 independent experiments. Asterisks denote student’s t test significant difference compared with that of DMSO (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).