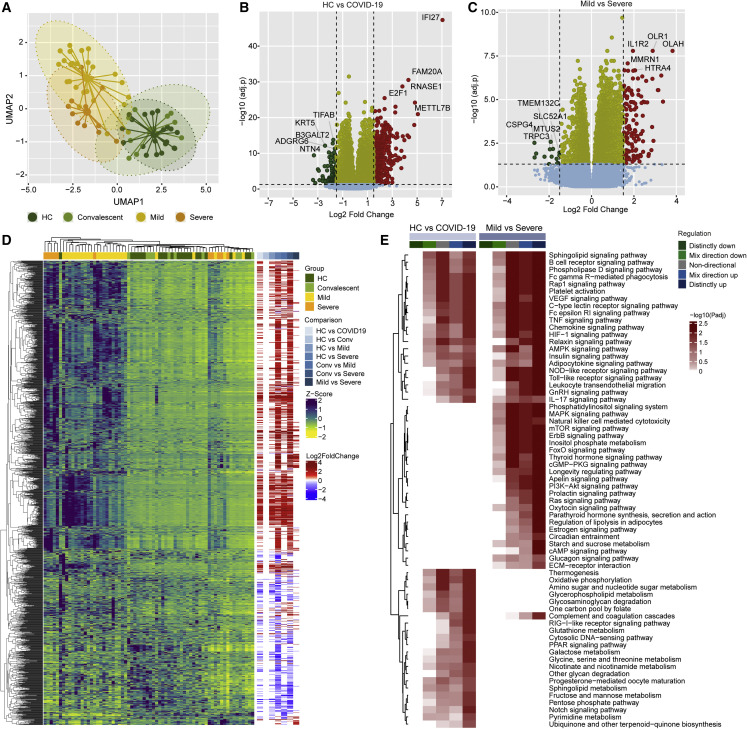
Figure 4.
System-wide transcriptomics profile in COVID-19 patients identified dysregulated immune and metabolic pathways
(A) Sample distribution using normalized transcriptomics data (log2 counts per million) of all protein-coding genes through UMAP, colored by cohort.
(B) Volcano plot visualizing gene expression changes in SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals (mild [n = 26] and severe [n = 11] in comparison with healthy individuals [HC, n = 21]). The top five significantly regulated genes are labeled.
(C) Volcano plot visualizing gene expression changes in SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals with severe COVID-19 (n = 11) in comparison with mild disease (n = 26). The top five significantly regulated genes are labeled.
(D) Heatmap visualizing expression pattern (Z score transformed log2 counts per million) and log2 scaled fold change values of significantly regulated genes in pairwise comparisons (adj. p < 0.05 and log2-fold change > 1.5). Column annotation represents patient groups, and pairwise differential expression comparisons and rows represent genes.
(E) Heatmap visualizing significantly regulated Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways (adj. p < 0.05) in SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals (mild [n = 26] and severe [n = 11] in comparison with healthy individuals [HC, n = 21]) and COVID-19 patients with severe disease (n = 11) in comparison with patients with mild disease (n = 26). The color scale represents negative log10 scaled adjusted p values of different directionality regulation classes. The non-directional p values are computed from the gene statistics disregarding the direction of expression. Mix-direction down and mix-direction up p values were computed by considering the segment of the gene statistics that are downregulated and upregulated, respectively. Distinct-directional p values were calculated using expression direction along with gene statistics. The distinct-direction up p values is exclusively influenced by the upregulation of genes. By contrast, distinct-direction down p values is influenced by downregulation of genes and not influenced by upregulation and downregulation together.