Figure 2.
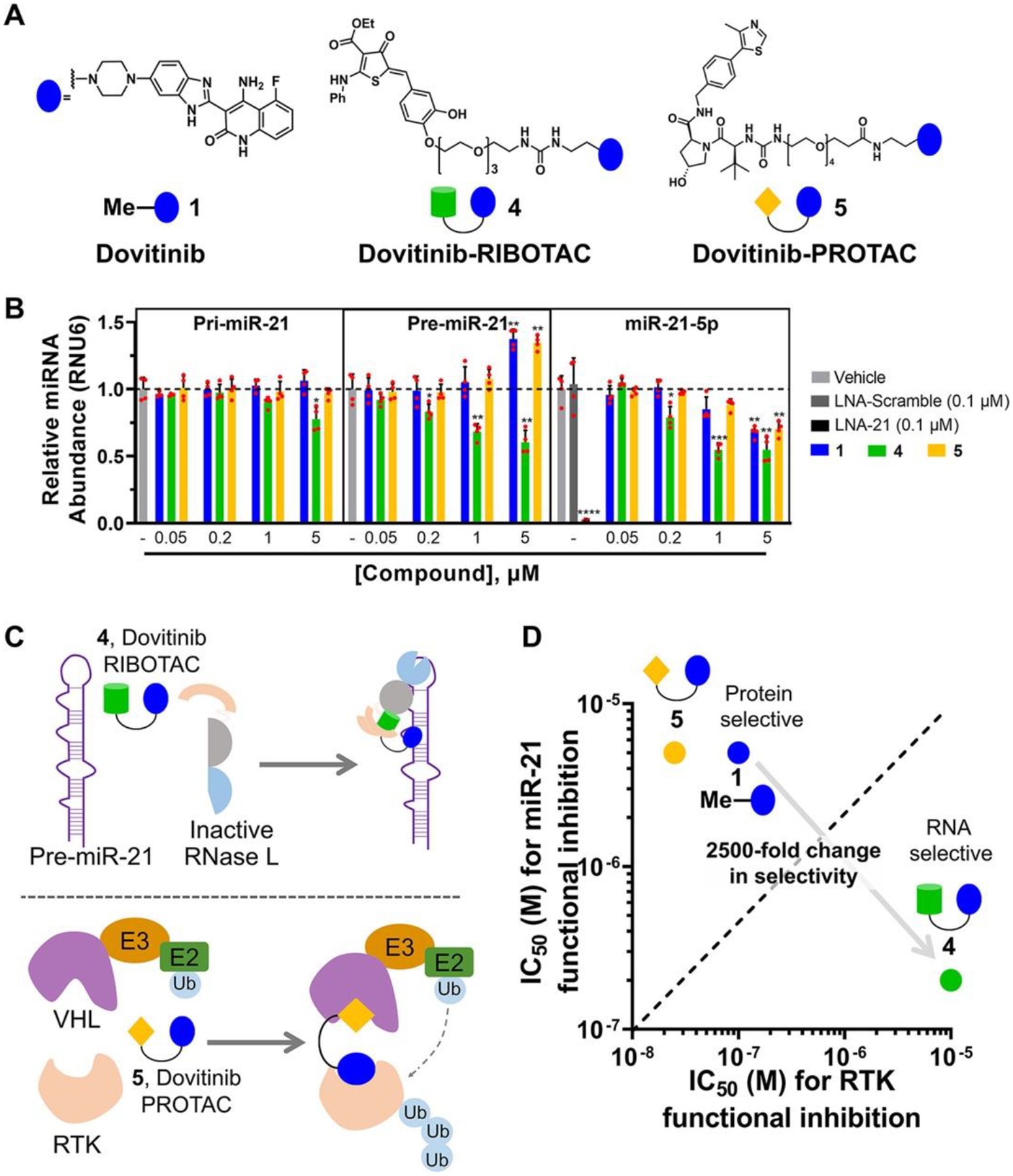
Dovitinib-based rational design of a RIBOTAC for RNA and a PROTAC for protein. (A) Structures of parent compound 1, RIBOTAC 4, and PROTAC 5. (B) Compounds 1, 4, and 5 reduced mature miR-21 levels in the TNBC cell line MDA-MB-231, as determined by RT-qPCR analysis (n = 4). RIBOTAC 4 decreased pre-miR-21 levels via RNase L cleavage, while 1 and 5 increased pre-miR-21 levels, consistent with their mode of action, binding and inhibiting Dicer cleavage. Compounds 1, 4, and 5 (up to 1 μM) had no significant effect on pri-miR-21 levels in MDA-MB-231 cells, as determined by RT-qPCR (n = 4). Compound 4 had a modest effect on pri-miR-21 levels at 5 μM (n = 4). (C) Scheme of RIBOTAC 4 dimerizing RNase L onto pre-miR-21 to cleave it enzymatically (left) and PROTAC 5 recruiting VHL onto an RTK to induce its ubiquitination, leading to subsequent proteasome-mediated down-regulation (right). (D) RIBOTAC 4 exhibited 25-fold increased miR-21 inhibitory activity and 100-fold decreased RTK inhibition, both as compared with 1, while 5 exhibited similar miR-21 inhibitory activity and 5-fold increased RTK inhibition. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, as determined by a two-tailed Student’s t test.
