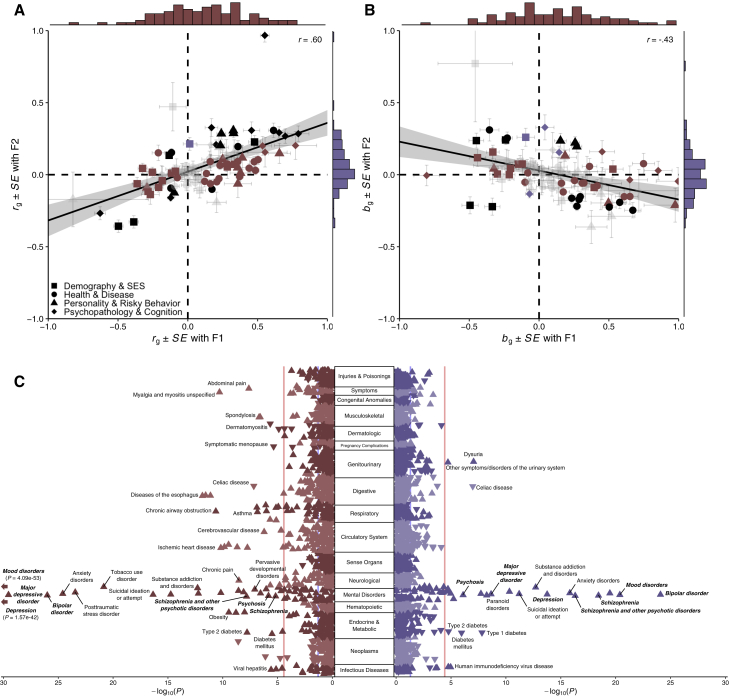
Figure 5.
Genetic-correlation and phenome-wide association results for the two transdiagnostic latent genetic factors
(A) Scatterplot of genetic correlations (rg) with marginal histograms.
(B) Scatterplot of partial genetic correlations (bg) with marginal histograms. For both plots, phenotypes are grouped into one of four broad domains: (1) demography and socioeconomic status, (2) health and disease, (3) personality and risky behavior, and (4) psychopathology and cognition. A line of best fit (with 95% confidence interval) is fit for all 92 data points. Points are colored burgundy if significant only for F1, violet if significant only for F2, black if significant for both, and faded gray if non-significant for both. The standard errors (SEs) for point estimates are plotted for both factors.
(C) Rotated Miami plot for (left) F1 and (right) F2, where the y axis refers to the ICD-10 code category, the x axis refers to the significance on a −log10 scale, the vertical light red line denotes phenome-wide significance (p = 3.27 × 10−5) following Bonferroni correction, and the vertical light blue line marks nominal significance (p = 0.05). The direction of the triangle refers to the direction of effect. Phecodes closely resembling Genomic SEM model phenotypes are bolded and italicized for emphasis.