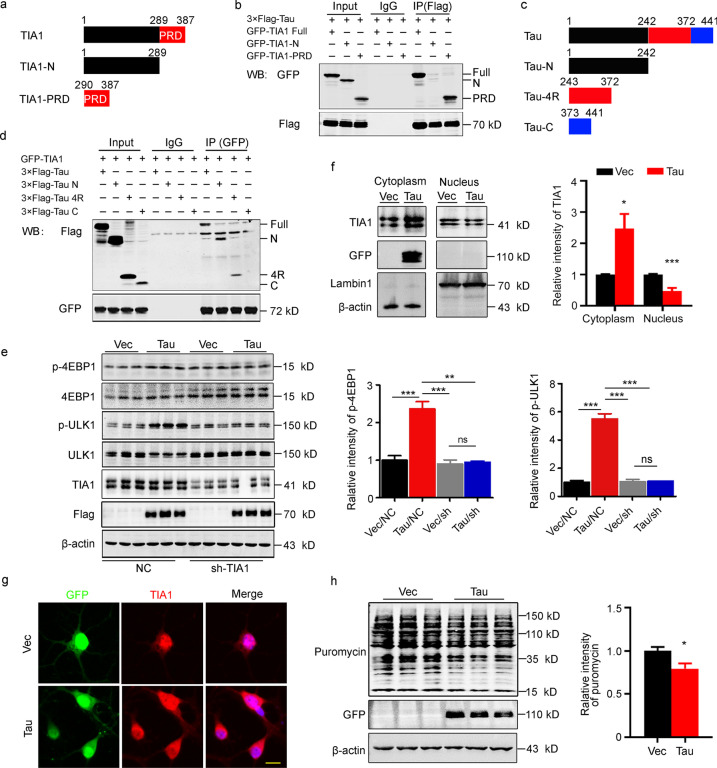
Fig. 5.
N-terminal tau binds to PRD-TIA1 to detain TIA1 in the cytoplasm and inhibit protein synthesis. a Schematic showing full-length TIA1, N-terminal TIA1 and the PRD of TIA1. b Tau could interact with TIA1 at its PRD domain as detected by coimmunoprecipitation in HEK293T cells. c Schematic showing constructs of full-length tau, N-terminal tau, four microtubule-binding repeats of tau, and C-terminal tau. d Tau-N and tau-4R but not Tau-C could efficiently bind TIA1, which was detected by coimmunoprecipitation in HEK293T cells. e N2a cells were cotransfected with 3 × Flag-tau and sh-TIA1 plasmids. The attenuated levels of p-4EBP1 and p-ULK1 in the tau/shTIA1 group were detected by Western blotting (n = 9). f N2a cells were transfected with eGFP-tau plasmids. The protein level of TIA1 was increased in the cytoplasm, while was decreased in the nucleus in the tau-OE group, as detected by Western blotting (n = 6). g Hippocampal neurons were infected with Lenti-eGFP-P2A-tau or Lenti-eGFP-P2A-C1, and the increased cytoplasmic localization of TIA1 (Red) was imaged by immunofluorescence staining (scale bar = 20 μm). h Decreased level of protein synthesis in N2a cells that transiently transfected with eGFP-tau plasmid was detected by Western blotting using an anti-puromycin antibody (n = 9). 4EBP1 the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1, 4R four microtubule-binding repeats of tau, C C-terminal, GFP green fluorescent protein, IP immunoprecipitation, N N-terminal, NC normal control, ns non-significant, PRD prion-related domain, TIA1 T cell intracellular antigen 1, ULK1 unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase 1, Vec vector. All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001