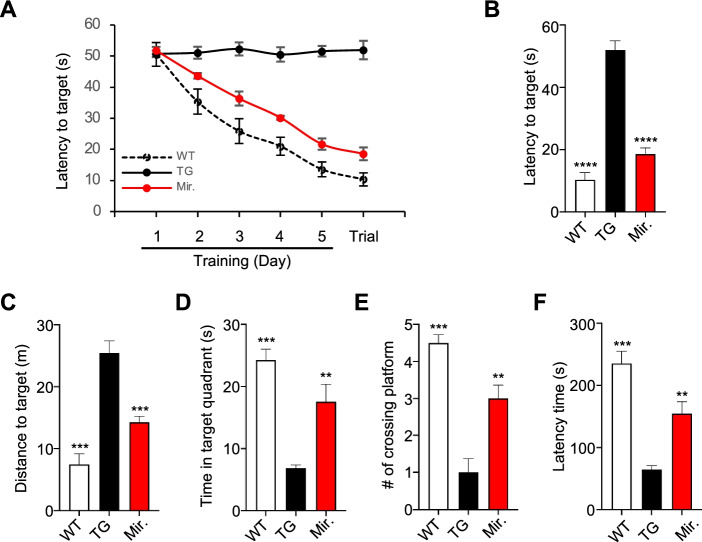
Fig. 1.
Mirodenafil improves cognitive function in the APP-C105 AD mice. A Mean latencies for the training session and visible platform trials in the Morris water maze (n = 6) B–D Morris water maze test was performed to test hippocampus-dependent learning and memory functions in 13-month-old male vehicle-treated wild-type (WT), vehicle-treated APP-C105 transgenic (TG), and mirodenafil-treated APP-C105 transgenic (Mirodenafil) mice, after 4 weeks of administration. Mirodenafil (4 mg/kg) in PBS was administered daily via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection to 13-month-old male APP-C105 transgenic mice (n = 6) for 4 weeks. PBS vehicle solution was administered to age-matched male WT (n = 6) and transgenic (n = 6) mice. B Latency to target, C distance to reach target, D time in target quadrant, and E number of platform crossings were measured. To evaluate fear-conditioned learning and memory, APP-C105 mice were subjected to the passive avoidance test, and mirodenafil was administered by i.p. injection (4 mg/kg) for 4 weeks before the training trial. F Passive avoidance test. Latency to enter dark the compartment among WT, TG, and mirodenafil mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 4; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons