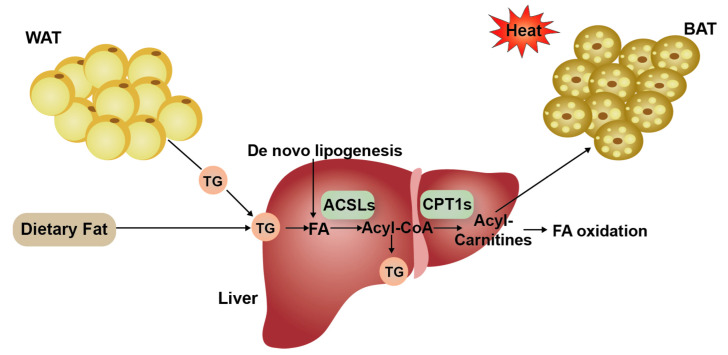
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of liver fatty acid (FA) oxidation. Liver FAs are mainly derived from dietary lipids, adipose tissue decomposition, and de novo synthesis. FAs are activated by long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases (ASCL) to form acyl-CoA molecules, which can undergo oxidation or be incorporated into complex lipids. Acyl-CoA is transferred to mitochondria by carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), and then, Acyl-CoA converts Acyl-Carnitines, which can partition to brown adipose tissue (BAT) for heat generation or continually into FA oxidation.