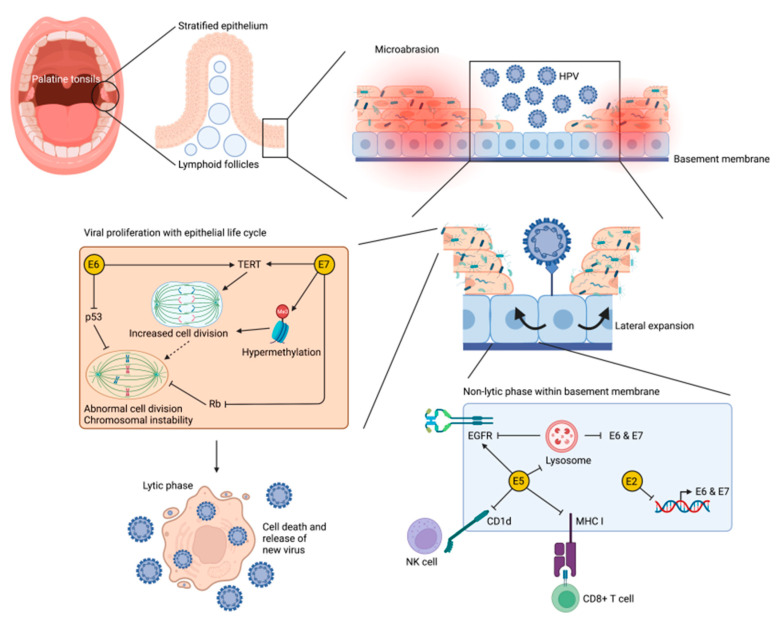
Figure 2.
Interplay of HPV, the microbiome, and the oropharynx. Overview of the HPV lifecycle within a tonsillar tumor. Microabrasions in tonsillar epithelium lead to HPV infection of basilar and epithelial cells. Basilar cells undergo lateral expansion during the non-lytic phase of the viral cycle, primarily mediated by E5 [43]—which modulates EGFR signaling [44], downregulates CD1d [45], prevents MHCI trafficking [46], and regulates autophagy [47]. Epithelial cells undergo proliferation and transformation prior to the lytic phase of the virus’s life cycle, primarily mediated by E6 (which degrades p53) and E7 (which similarly degrades Rb) [48]. E6 and E7 also affect cell division via TERT and methylation [49,50]. Figure generated using BioRender.