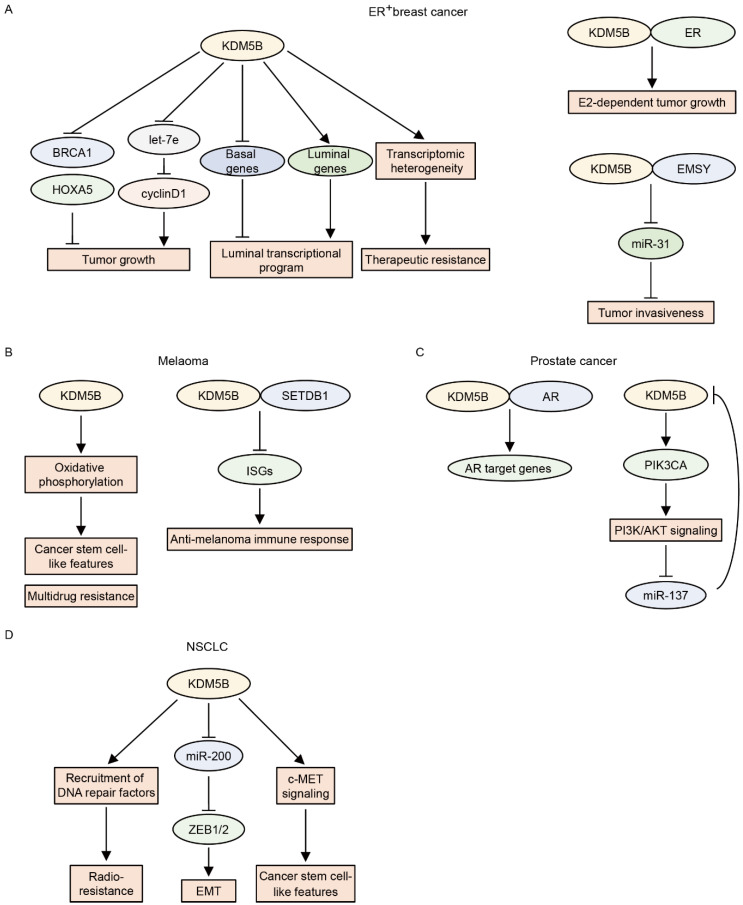
Figure 4.
The functions of KDM5B in each type of cancer. (A) In estrogen receptor (ER)+ breast cancer, KDM5B promotes tumor growth by repressing BRCA1 and HOXA5 and by inducing cyclin D1 through the repression of let-7e. KDM5B induces the luminal transcriptional program by downregulating basal genes and upregulating luminal genes. KDM5B also contributes to therapeutic resistance by inducing transcriptomic heterogeneity. KDM5B and ER coordinately stimulate E2-dependent tumor growth. KDM5B and EMSY induce tumor invasiveness by repressing miR-31. (B) In melanoma, KDM5B induces cancer stem cell-like features and multidrug resistance by promoting oxidative phosphorylation. KDM5B also inhibits the anti-melanoma immune response by repressing interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) in cooperation with SETDB1. (C) In prostate cancer, KDM5B activates androgen receptor (AR) target genes in cooperation with AR. KDM5B also activates PI3K/AKT signaling by upregulating PIK3CA. PI3K/AKT signaling suppresses miR-137, which consequently increases KDM5B expression, forming a positive feedback loop. (D) In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), KDM5B induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by increasing ZEB1 and ZEB2 through repressing the miR-200. KDM5B also confers radioresistance by recruiting DNA repair factors to DNA damage sites. In addition, KDM5B induces cancer stem cell-like features by activating c-MET signaling.