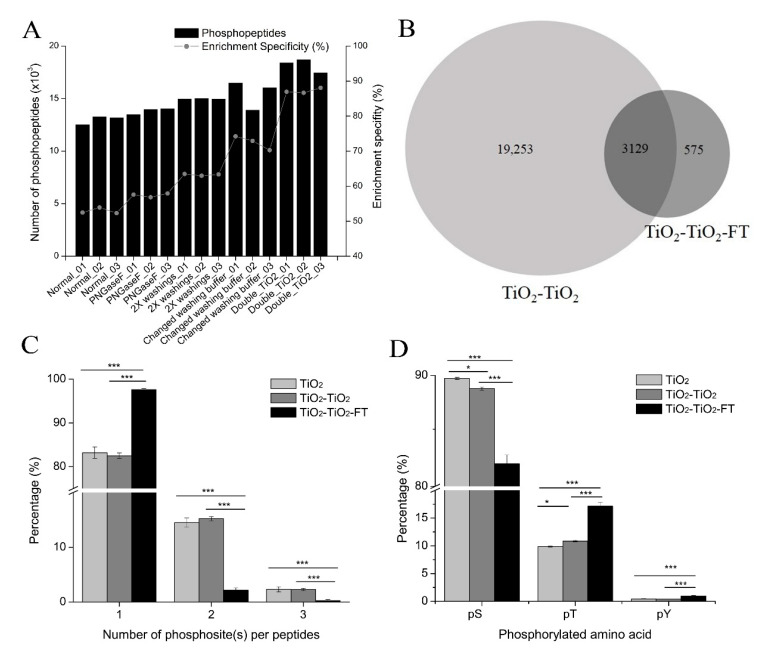
Figure 4.
Improved phosphopeptide enrichment protocols with TiO2 using glycolic acid. (A) Profiles of the number of phosphopeptides identified and phosphopeptide enrichment specificity with the four modified phosphopeptide enrichment protocols that used glycolic acid. Three replicates are performed for each protocol. “Normal” represents the normal phosphopeptide enrichment protocol using glycolic acid; “PNGaseF” represents that PNGaseF is used to remove glycans from peptides before TiO2 enrichment; “2X washings” represents that the volume of the loading and washing buffers is double that of the normal phosphopeptide enrichment protocol; “Changed washing buffer” represents that different washing buffers are used during phosphopeptide enrichment; “Double_TiO2” represents that two rounds of TiO2 enrichment are performed for each experiment. (B) Overlap between phosphopeptides identified in TiO2-TiO2 (double TiO2 enrichment) and TiO2-TiO2-FT (the supernatant of double TiO2 enrichment). The combined results of three replicates are shown. (C) The percentage of singly phosphorylated, doubly phosphorylated, and triply phosphorylated peptides in TiO2 enrichment (normal phosphopeptide enrichment protocol using glycolic acid), TiO2-TiO2 enrichment, and TiO2-TiO2-FT. Bars show mean ± SD of three replicates; *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test). (D) The percentage of phosphorylated amino acids (serine(pS), threonine (pT), and tyrosine (pY)) in TiO2 enrichment, TiO2-TiO2 enrichment, and TiO2-TiO2-FT. Bars show mean ± SD of the three replicates; * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test).