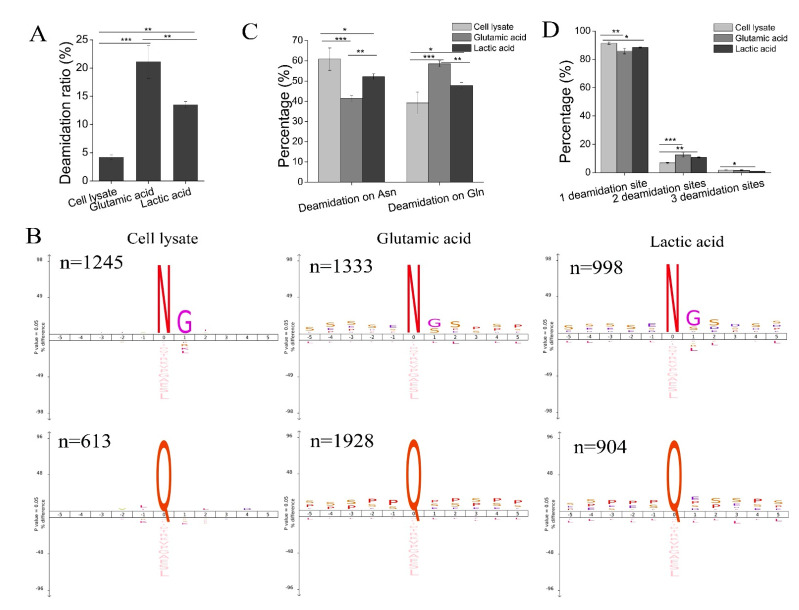
Figure 5.
Deamidation of phosphopeptides. (A) The deamidation ratio (measured by the ratio of deamidated (phospho)peptides to all (phospho)peptides identified) in peptides identified from cell lysate, and phosphopeptides identified with the glutamic acid method and the lactic acid method. Bars show mean ± SD of the three replicates; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test). (B) The iceLogo sequence motif analysis of residues flanking deamidation sites in peptides identified from cell lysate (left), and phosphopeptides identified from the glutamic acid method (middle) and the lactic acid method (right) (p < 0.05). The height of amino acid letters corresponds to the percentage. N represents amino acid asparagine; Q represents amino acid glutamine; G represents amino acid glycine; S represents amino acid serine. (C) The percentage of deamidation sites (deamidation on Asn or Gln) in peptides identified from cell lysate, and phosphopeptides identified from the glutamic acid method and the lactic acid method. Bars show mean ± SD of the three replicates; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test). (D) The number of deamidation sites in peptides identified from cell lysate, and phosphopeptides identified with the glutamic acid method and the lactic acid method. Bars show mean ± SD of the three replicates; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test).