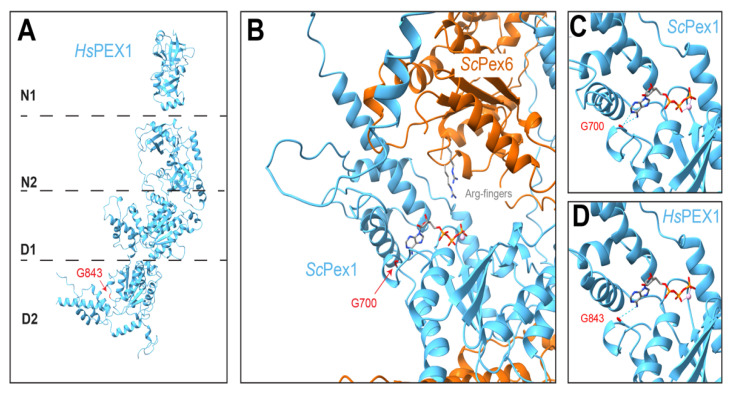
Figure 7.
PEX1 G843D is expected to disrupt ATP binding and/or protomer folding. (A) HsPEX1, based on AlphaFold2 and X-ray crystallography (as in Figure 2, PDB 1WLF, [148]). G843 is in the PEX1 D2 ring. (B) ScPex1 D2 ATPase in the Pex1/Pex6 hexamer at the Pex1 site most likely to be nucleotide-bound (AlphaFold2, EMDB-6359, [143]). Note that nucleotides are not discernible in experimental structures of Pex1/Pex6; an ATP is modeled based on alignment with a high-resolution structure of Hsp97 (PDB 7LN5, [159]). (C) The glycine G843 in HsPEX1 is conserved. The homologous residue in ScPex1 (G700) is colored in red and the backbone is predicted to hydrogen bond with the adenosine of ATP ([159], ChimeraX). (D) In the structurally similar ScPex1 and HsPEX1 ATPase sites, G700 or G843 hydrogen bond (dotted lines) with ATP.