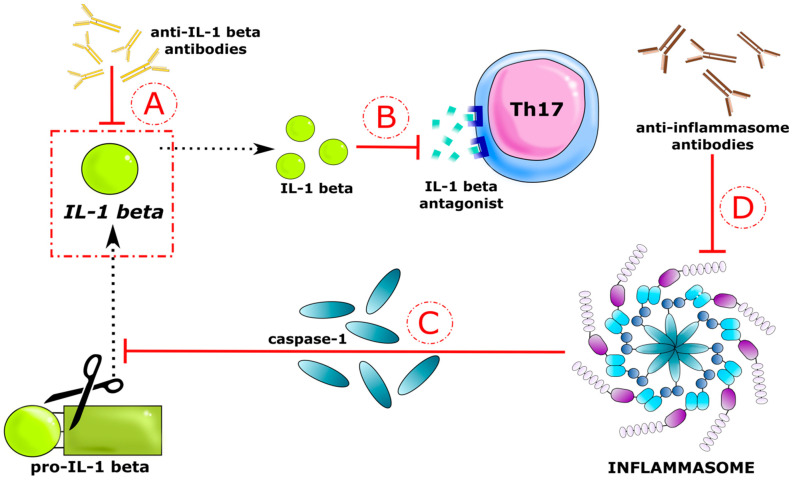
Figure 7.
IL-1 beta as a therapeutic target in reducing the allergic inflammatory response. The red arrows represent the likely therapeutic impact sites. IL-1 beta is a highly pro-inflammatory cytokine that has been found to increase in children with IgE-mediated food allergy (FA) and atopic dermatitis (AD). IL-1 beta secreted by cells in an inactive form as pro-IL-1 beta is activated by caspase-1 released from the inflammasome. It acts through two receptors to trigger the polarization of naive Th cells into the Th17 lineage. We propose four therapeutic approaches at each stage of IL-1 beta formation and an action to reduce the inflammatory response. (A) Direct blockage of IL-1 beta by anti-IL-1 beta antibodies; (B) blockage of the IL-1 beta receptor by the antagonist; (C) neutralization of caspase-1, which is the pro-IL-1 beta activating enzyme; (D) inactivation of inflammasomes.