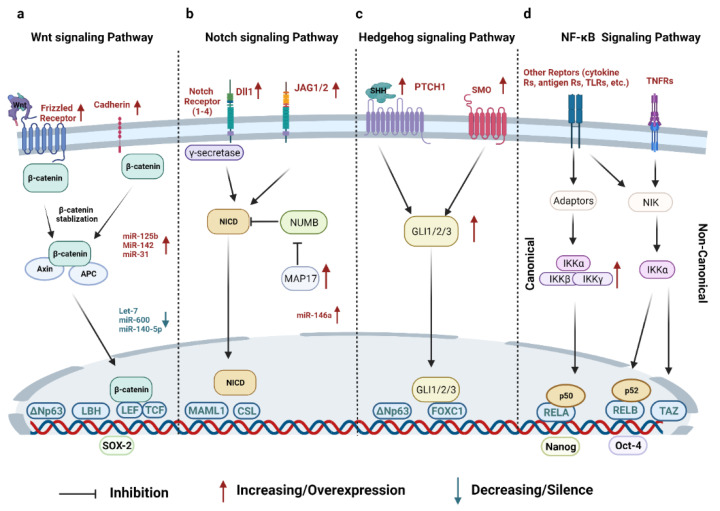
Figure 1.
Summary of important signaling pathways in BCSCs. (a) The Wnt signaling pathway is activated when Wnt ligands bind to the receptor complex, which dissociates β-catenin from the destruction complex and activates β-catenin as the transcriptional co-activator within the LEF/TCF transcriptional complex. In BCSCs, several frizzled receptors are upregulated and several miRNAs are altered in expression. (b) The Notch signaling pathway is induced by juxtacrine interactions between Dll or JAG1/2 and Notch receptors, resulting in the release of NICD as the transcription factor for activation of a panel of genes. The expression of Dll and JAG1/2 ligands can be elevated from several cellular sources within the BCSC microenvironment to induce juxtacrine activation of Notch signaling in BCSCs. MAP17 inhibits NUMB, the antagonist of NICD, to activate Notch signaling pathway in BCSCs. (c) The activation of HH signaling pathway initiates from HHs binding to the PTCH receptor, leading to the de-repression of SMO. The GLI 1/2/3 translocate to the nucleus and form the transcriptional complex to activate gene expression. In BCSCs, PTCH1, SMO, and GLIs are upregulated to enhance the HH signaling pathway. (d) The canonical NF-κB signaling pathway is initiated from various receptors including TNFR, which activates the trimeric IKK complex via several steps. The IKK complex induces the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of IκBα, which results in the nuclear translocation of canonical NF-κB dimer RelA/p50. The non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway can also be initiated by several TNFR superfamily members such as RANKL. NIK and IKKα are required for propagating non-canonical signaling pathways. This process induces the degradation of p100, leading to the generation of the RELB/p52 dimer that translocates to the nucleus. In BCSCs, the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway is associated with BCSC self-renewal and the expression level of BCSC markers. Moreover, some crucial transcription factors, such as Oct-4, Nanog, and SOX2, are consistently activated in BCSCs to maintain their self-renewal capacity. Key abbreviations: APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; LBH, limb bud-heart; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; MAML1, mastermind-like transcriptional co-activator 1; CSL, CBF1, suppressor of hairless, lag-1; GLI 1/2/3, GLI Family Zinc Finger 1/2/3; FOXC1, forkhead box C1; NIK, NF-κB-inducing kinase; IKK, inhibitor of κB kinases.