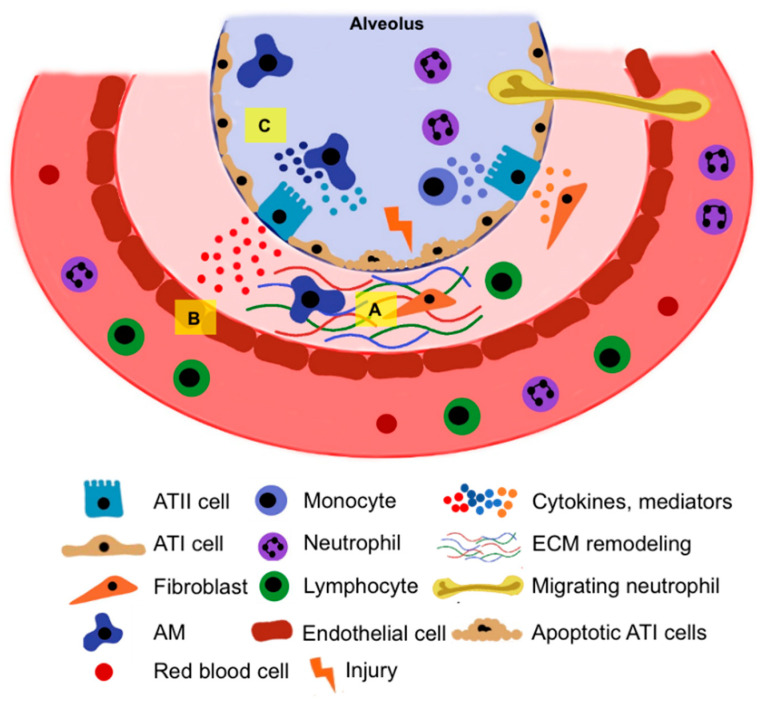
Figure 1.
Various cell types are part of the ATII cell niche, providing a specific microenvironment to support alveolar re-epithelialization after injury. (A) Mesenchyme, including fibroblasts, extracellular matrix (ECM), and pericytes around endothelium and alveoli, can sense microenvironmental changes and mechanical stress and interact with alveolar epithelium, contributing to tissue remodeling. (B) Activated endothelial cells proliferate and regulate alveolar epithelial cell repair after injury to maintain alveolar–capillary function and integrity. (C) Immune cells are a component of the regenerative alveolar type II (ATII) cell niche. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are important in innate immunity, regulating adaptive immunity, and recruiting neutrophils and monocytes into the lungs. They defend against pathogens while supporting ATII cell proliferation and differentiation to alveolar type I (ATI) cells. Together, various reciprocal interactions, transcription factors, mediators, and signaling pathways among different cell types orchestrate complex lung repair and homeostasis.