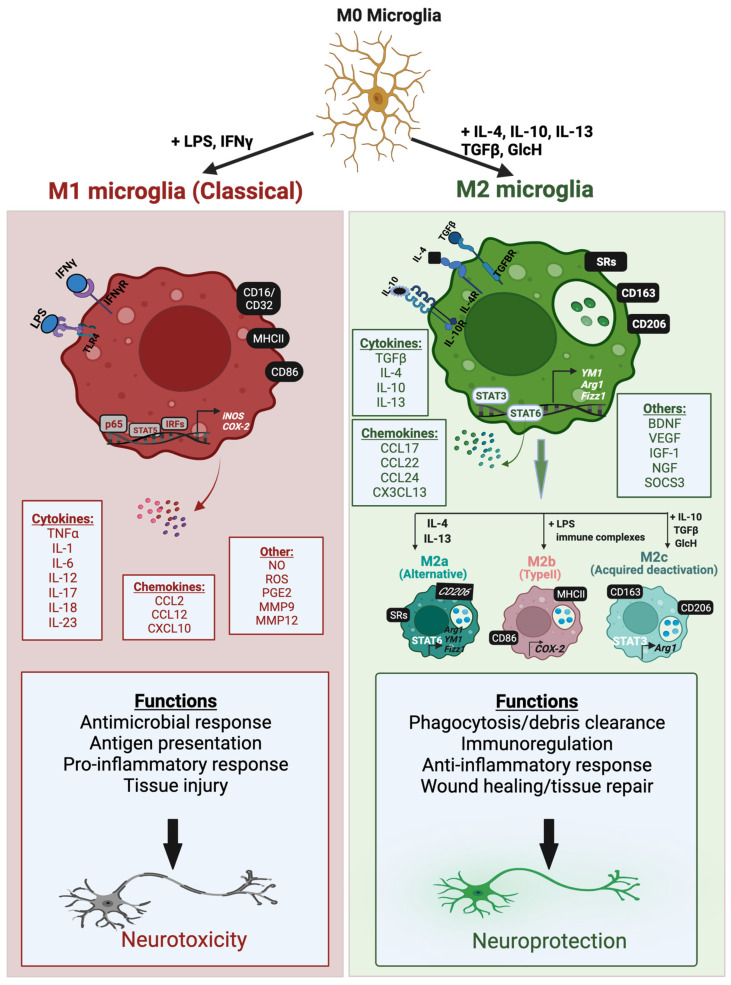
Figure 1.
Microglial activation phenotypes and functions. Microglia can be polarized from a resting state (M0 microglia) to two main activation phenotypes, classically activated M1 microglia and alternatively activated M2 microglia, which are induced by interaction of inflammatory molecules with their respective cognate receptors. These microglia phenotypes exhibit a variety of phenotypic markers that are expressed intracellularly or on the cell surface, as well as molecules that are secreted from the cell, such as chemokines, cytokines, and other effector molecules. The M2 phenotype is further subdivided into three subtypes: M2a (alternatively activated state), M2b (type II activation phenotype), and M2c (acquired deactivation state). The M2b subtype shares similar features as M1 microglia and is induced by inflammatory molecules. The phenotypes of M1 and M2 microglia perform distinct functions that can be neurotoxic or neuroprotective, respectively. Figure created using BioRender.com (accessed on 14 April 2022).