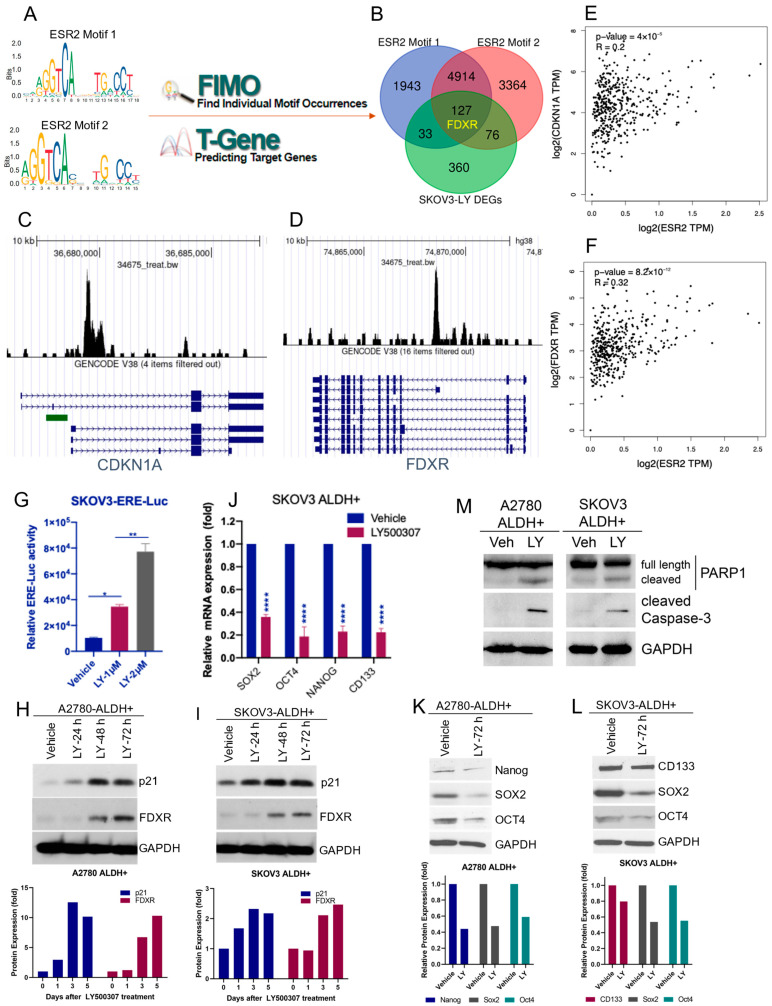
Figure 4.
In silico analysis suggested FDXR and CDKN1A could be direct targets of ERβ. (A) Exploration of potential ERβ target genes. Motifs of ESR2 (ERβ) were acquired from JASPAR and mapped with the FIMO and T-Gene modules from the MEME Suite in sequence. (B) Potential ERβ target genes were identified by the intersection of potential target genes with LY500307-regulated DEGs in OCSCs, including FDXR. (C,D) ChIP-seq profiles from CistromeDB confirmed enrichment of ERβ at CDKN1A and FDXR gene promoters. (E,F) Co-expression analysis using GEPIA2 showed CDKN1A and FDXR expression are positively correlated with ESR2 expression. (G) SKOV3 cells stably expressing ERE-luc reporter plasmid were cultured as spheroids for 7 days and treated with vehicle or LY500307 for 24 h. ERE-luc reporter activity was measured using a Luciferase Assay System. (H,I) SKOV3- and A2780- ALDH+ve cells were treated with LY500307 and harvested at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after treatment and p21 and FDXR expression was determined by Western blotting. Relative protein band intensity of representative blots was quantitated using NIH ImageJ software and shown in bottom panels. (J) SKOV3 ALDH+ve cells were treated with vehicle or LY500307 for 72 h and stemness marker expression was determined using RT-qPCR. (K–M) SKOV3- and A2780- ALDH+ve cells were treated with vehicle or LY500307, and expression of stemness (Nanog, SOX2, OCT4, and CD133) and apoptotic markers (cleaved PARP1 and Caspase-3), respectively, was determined using Western blotting. Data are represented as mean ± SE. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; **** p < 0.0001.