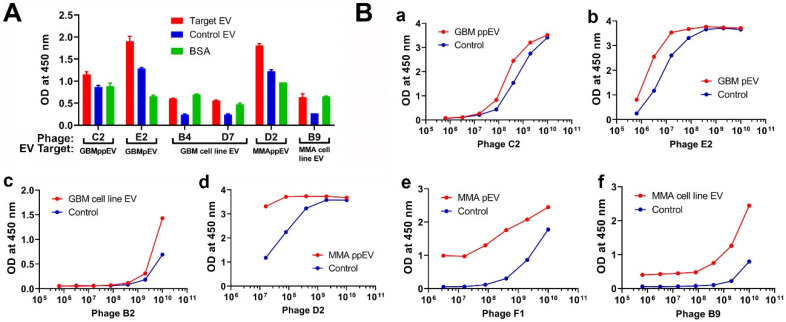
Figure 2.
ELISA demonstrates that phage peptides selected by brain tumor extracellular vesicles are specific to panning EVs. (A) Direct ELISA shows that phage peptides are specific to panning brain tumor EVs. The target EVs include GBM and MMA ppEVs (from pooled plasma), pEVs (from individual plasma), and tumor cell line EVs. EVs coated on a high-binding ELISA plate (50 mg/mL) were incubated with corresponding phage (2 × 109 pfu/well). Bound phage peptides were detected by mouse anti-M13 pIII-HRP antibody (1:5000 dilution) followed by TMB substrate color detection. Each representative phage peptide (labeled in letters) was shown for OD values to corresponding panning EVs (target EV), control EVs, and BCA. (B) Dose–response ELISA demonstrating specific bindings of phage peptides to panning brain tumor EVs. GBM (B-a–c) and MMA EVs (B-d–f) (pooled plasma, individual plasma, and tumor cell line EVs) at 50 mg/mL were directly coated onto wells of ELISA plates, followed by incubation with corresponding phage peptides in serial 5-fold dilutions starting with 1 × 1010 pfu/well. Detection was the same as described above. HC plasma EVs were used as controls for brain tumor plasma EVs (a,b,d,e), and normal human astrocyte EVs were used as controls for brain tumor EVs (c,f).