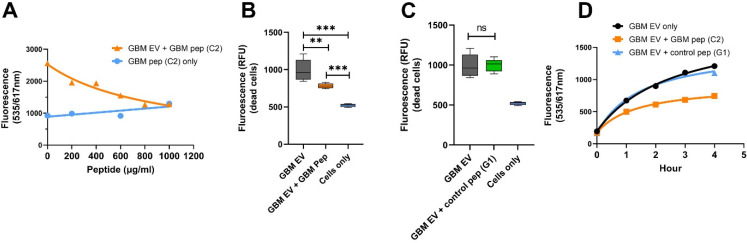
Figure 6.
GBM EV-specific peptides inhibit neuronal cytotoxicity induced by the GBM EVs. (A). GBM EV-specific peptide inhibits EV-induced neuronal cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner. SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with GBM pooled plasma EVs at 20 mg/mL plus 5% Normal Human Serum. GBM EV-specific peptide C2 in various amounts was added to cells at the same time as the EV treatment. Cell death was monitored by ethidium homodimer-1 (red fluorescent reading). With 1000 mg/mL peptide, the GBM EV peptide nearly completely blocked the GBM-EV cytotoxicity after 4-h treatment. Cells with peptides (C2) alone did not produce cytotoxicity. (B,C). GBM EV-specific peptides (B), but not the control peptides (C) show time-dependent inhibition of EV induced neuronal death. Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were treated with GBM EVs plus peptides, and cytotoxicity was monitored for 4 h. GBM EV-specific peptide C2 inhibited GBM-EV induced cytotoxicity (GBM EV + GBM Pep), but not the control peptide to HC EV (G1) (GBM EV + control pep G1) (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). (D) Time course of GBM-C2 peptide for the inhibition of GBM-EV cytotoxicity. SH-SY5Y cells were treated with GBM EVs at 20 mg/mL plus 5% Normal Human Serum. The GBM-C2 peptide (1000 mg/mL) or the HC-G1 peptide (as control, 1000 mg/mL) was added to cells during the same time as EV treatment. The cell death was monitored by propidium iodide red fluorescent reading once per hour. Results showed that the GBM peptide can inhibit GBM EV-induced cell death.