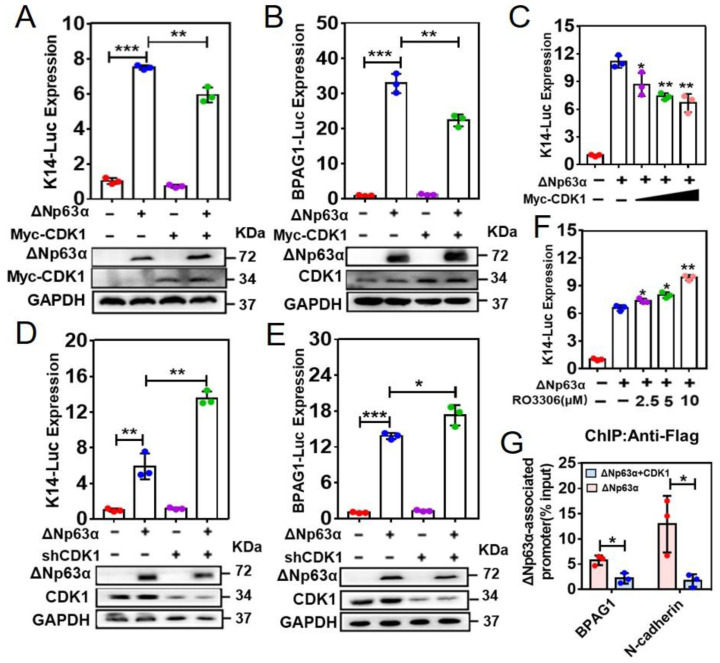
Figure 2.
CDK1 impairs association of ∆Np63α with its downstream gene promoters to inhibit ∆Np63α-mediated transcriptional regulation. (A–F), HEK293 cells were transfected with a mixture of K14- or BPAG1-Luc and TK-Renilla, plus Flag-∆Np63α and Myc-CDK1, shCDK1#1, increasing dose of Myc-CDK1 or RO3306 (a specific CDK1 inhibitor), as indicated. Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured, while IB analyses were performed to detect indicated proteins in parallel. The K14- or BPAG1-Luc expression levels were normalized to Renilla activity and presented as means ± SD (n = 3). Two-tailed t-test was used for comparison between two groups; ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. (G) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed with UM1 cells stably overexpressing Flag-∆Np63α or Flag-∆Np63α plus CDK1, using anti-Flag. DNA samples precipitated with either anti-Flag or mock IgG, as well as equivalent input, were subjected to quantitative polymerase chain amplification (qPCR) to detect fragments of BPAG1 and N-cadherin promoters. ∆Np63α-associated promoter fragments were assessed and normalized with input and mock IgG groups (means ± SD; n = 3; *, p < 0.05).