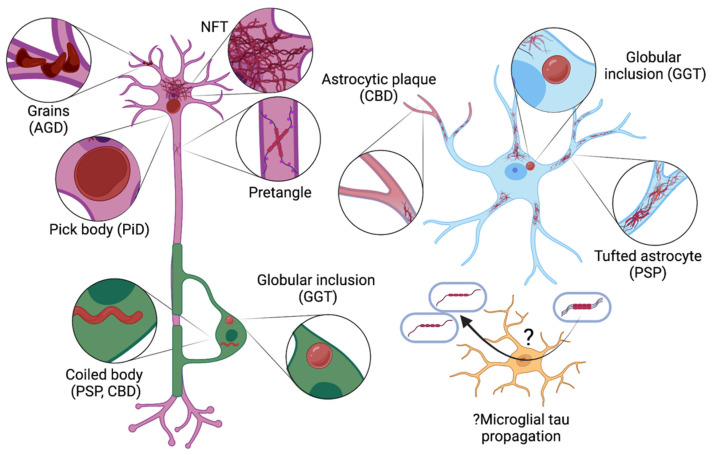
Figure 3.
Pathological tau lesions seen in different cell types in tauopathies. In the neuron (purple), tau aggregates include pretangles and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), round cytoplasmic inclusions (Pick bodies; typical of Pick disease [PiD]) and grains (dendritic swellings, seen in argyrophilic grain disease [AGD]). Oligodendrocytes (green) may develop tau aggregates in the form of globular inclusions (a feature of globular glial tauopathy [GGT]) or coiled bodies (seen in progressive supranuclear palsy [PSP] and corticobasal degeneration [CBD]). Tau may accumulate in astrocytes (blue) as star-like tufts, plaques, or globular inclusions (hallmarks of PSP, CBD, and GGT, respectively). While pathological tau lesions do not occur in microglia (yellow), they may be implicated in propagating tau (this uncertainty is indicated by the symbol ‘?’).