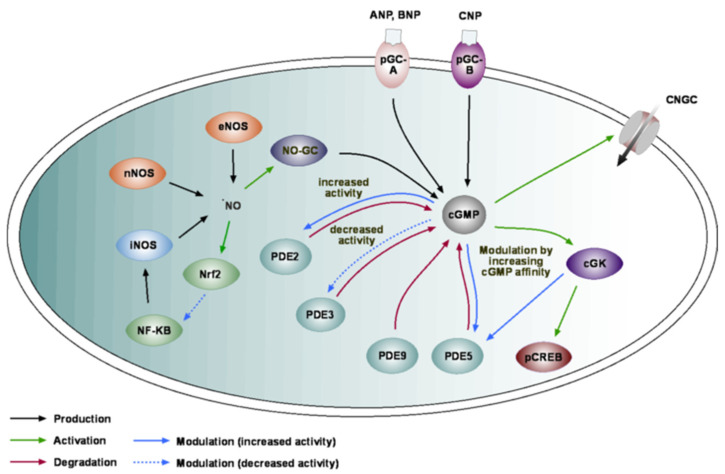
Figure 1.
cGMP signaling pathway. cGMP production is induced via activation of either NOS or natriuretic peptides (NPs). NO activates NO-GC in the cytosol, and pGC-A and pGC-B produce cGMP in the membranous fraction. cGMP stimulates cGK, which phosphorylates target proteins. cGMP is degraded by PDEs. PDE5 and 9 are cGMP-specific, and PDE1, 2, 3, and 10 are dual-substrate PDEs, degrading both cAMP and cGMP. NOS: nitric oxide synthase; iNOS: inducible NOS; eNOS: endothelial NOS; nNOS: neuronal NOS; NO-GC: soluble guanylate cyclase; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 cGMP: cyclic guanosine-3′,5′-monophosphate; NF-κB: nuclear factor κB; ANP: atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; CNP: C-type natriuretic peptide; pGC-A: particulate guanylate cyclase A; pGC-B: particulate guanylate cyclase B; cGK: cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase, also known as protein kinase G (PKG); PDE: phosphodiesterase; CNCG: cyclic nucleotide-gated channel; pCREB: phosphorylated cyclic adenosin monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding protein.