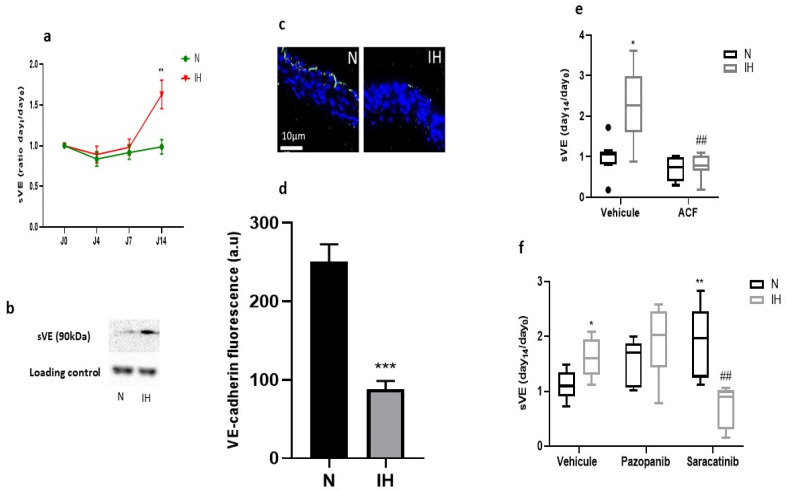
Figure 2.
Intermittent hypoxia impairs VE-cadherin integrity in vivo in C57BL/6J mice, which is prevented by inhibitors of VE-cadherin cleavage. (a) IH increased sVE level in the plasma of C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle (DMSO) after 14 days of exposure to IH, semi-quantitatively measured by Western blotting (N vs. IH at day 14, ** p < 0.01, Welch t-test, n = 21–22, values are mean ± SEM). (b) A representative example of Western blot showing a more intense sVE-band in the plasma of mice exposed to IH compared to those exposed to normoxia for 14 days (the immunoglobulin band is used as a loading control for normalization). (c) A representative example showing a more intense VE-cadherin fluorescence on the endothelium in N not in IH. Arrows indicate the VE-cadherin fluorescence in green in the endothelium, and the blue staining corresponds to nuclei stained with DAPI. (d) IH reduced VE-cadherin expression in the endothelium of C57BL/6J mice after 14 days of exposure to IH (N vs. IH at day 14, *** p < 0.001, Welch t-test, n = 15–16, values are mean ± SEM). (e) Inhibiting HIF-1 (by ACF) prevented the IH-induced elevation of sVE level in the plasma of C57BL/6J mice exposed for 14 days to IH or N (Kruskal-Wallis test, * p < 0.05 vs. N + vehicle, ## p < 0.01 vs. IH + vehicle, n = 6–8, values are median + interquartile range). (f) Inhibiting VEGFR tyr-kinases (by pazopanib) or src-kinases (by saracatinib) prevented the IH-induced elevation of sVE level in the plasma of C57BL/6J mice exposed for 14 days to IH or N (Kruskal-Wallis test, * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. N + vehicle, ## p < 0.01 vs. IH + vehicle, n = 5–8, values are median + interquartile range). N: normoxia, IH: intermittent hypoxia.