Fig. 5.
Exosome biosynthesis.
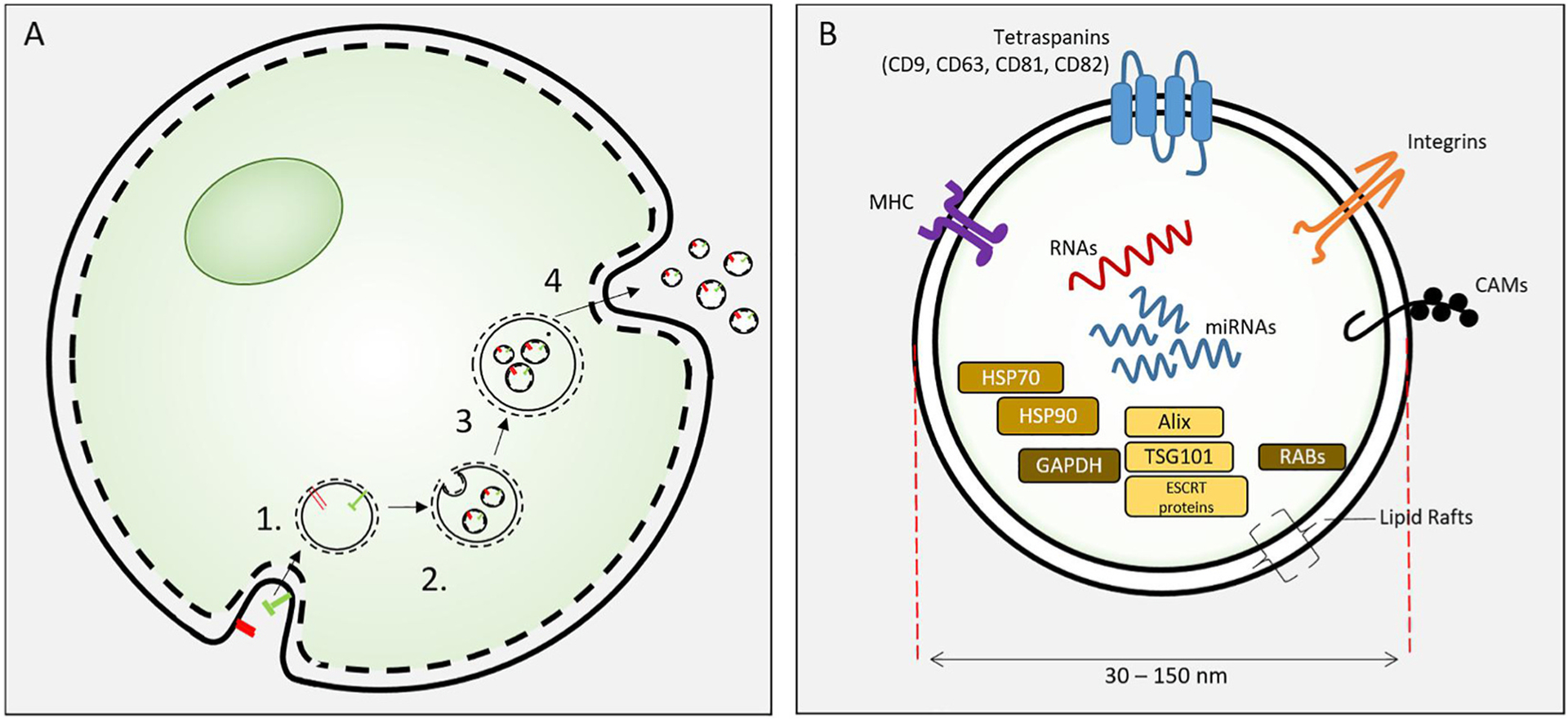
(A). Exosome biosynthesis. Exosomes are formed from endosomes [1] by an inward budding process to form intracellular vesicles [2]. These mature as multivesicular bodies [3] that fuse with the cell plasma membrane to release exosomes. (B) Exosomes are 30–150 nm extracellular vesicles containing specific proteins, RNAs and lipids. Proteins include HSP70, 90, GAPDH; proteins involved in synthesis (e.g. Alix, endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins, TGS101), and membrane associated or transmembrane proteins (RABs, Annexins, CAMs, Integrins, Tetraspanins, MHC I and II) and other cytosolic proteins. Figure from Cooper et al. reproduced with permission [146].
