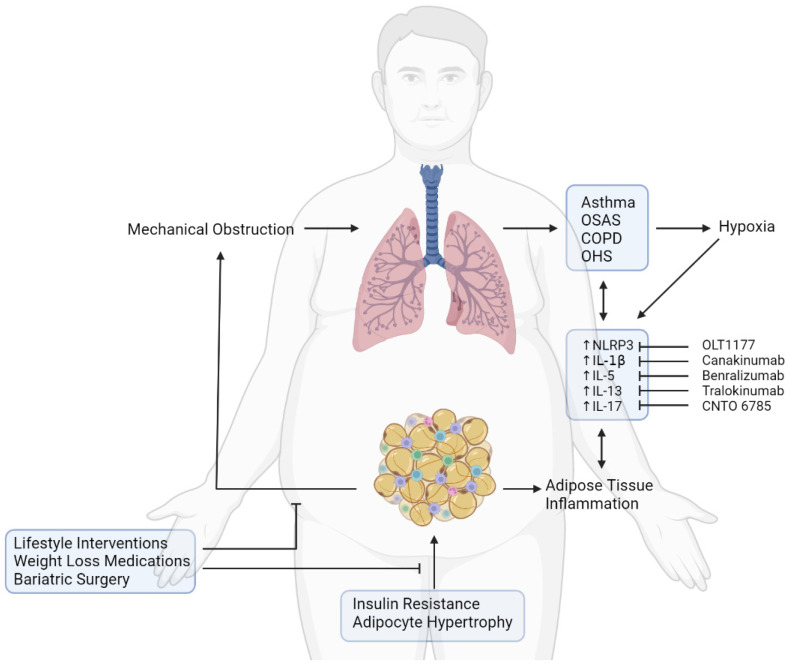
Figure 2.
Effects of obesity on pulmonary function and therapeutic strategies for the treatment of lung diseases. Insulin resistance and adipocyte hypertrophy induce adipose tissue inflammation. Excess of adipose tissue is responsible for mechanical obstruction of lung airways, promoting development of asthma, OSAS, COPD, and OHS, which are responsible for hypoxia. Both hypoxia and adipose tissue inflammation foster activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, increasing levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-5, IL-13, IL-17) and promoting development of lung diseases. Improvement in the respiratory function in people with obesity and lung disease could be achieved through therapeutic intervention for weight loss or through pharmacological strategies able to target the inflammasome and its downstream cytokines.