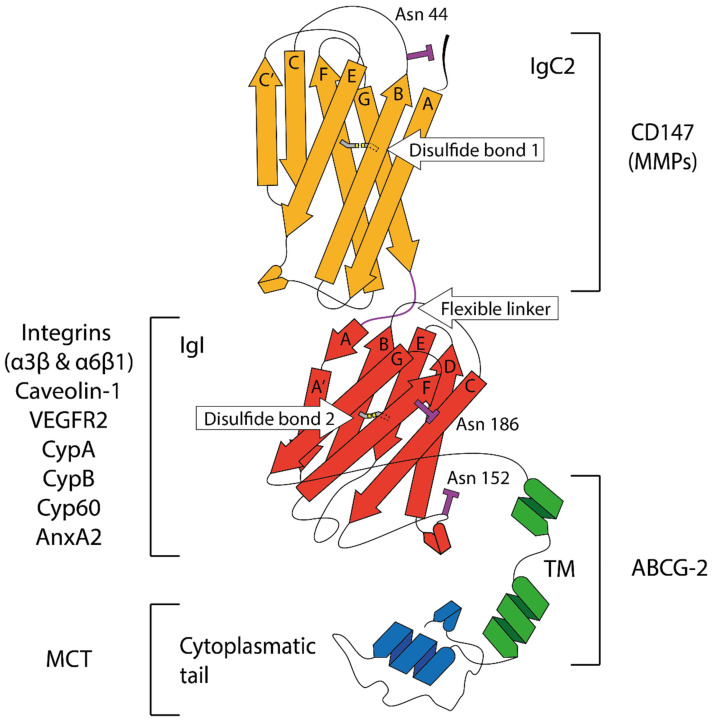
Figure 1.
Structure of CD147/bsg-2 with the two Ig domains (IgC2 and IgI) connected by a flexible linker, the transmembrane domain and the cytoplasmatic domain. The cartoon shows the diagrammatic representation of the molecular structure of CD147 and molecules potentially interacting with each domain based on previous reports [249,250,255]. Letters label molecular strands forming Ig domains. The N-terminal domain (IgC2, orange) has a disulfide bond connecting strand B and F (between C41 and C87, respectively) and an N-linked glycosylation site at Asn-44 at the end of strand B. This domain is responsible for homophilic interactions and influences MMP activity. The C-terminal domain (IgI, red) has a disulfide bond connecting B and F strand (between C126 and C185, respectively) and two potential glycosylation sites at Asn-152 and Asn-186. The flexible linker is shown in purple, the transmembrane domain (TM) in green and the cytoplasmatic domain in blue.