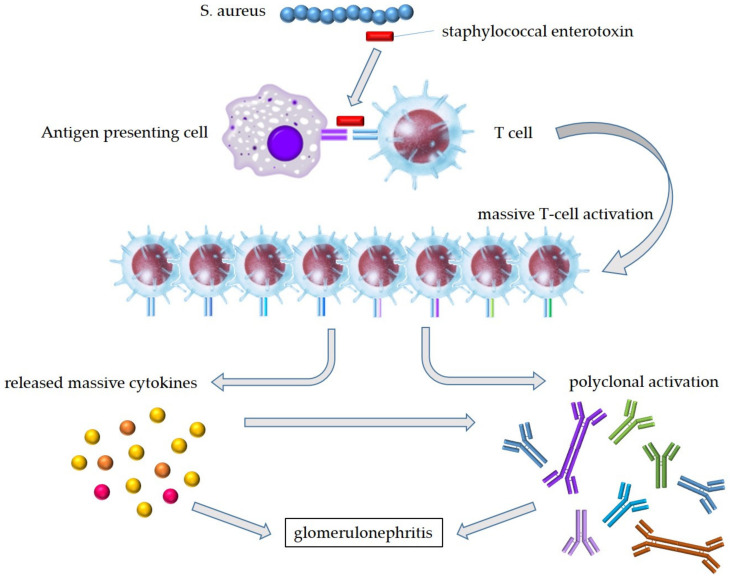
Figure 4.
Hypothesis of pathogenesis in SAGN with IgA-dominant deposition. Staphylococcal enterotoxins produced by S. aureus bind to specific TCR-Vβ on T cells and the outer part of the MHC molecules without being processed. Bacterial superantigens lead the MHC-unrestricted huge T-cell activation. The subsequent excessive release of cytokines activates not only T cells but also B cells; the polyclonal immunoglobulin production leads to the formation of immune complexes, resulting in the onset of SAGN. S. aureus—Staphylococcus aureus.