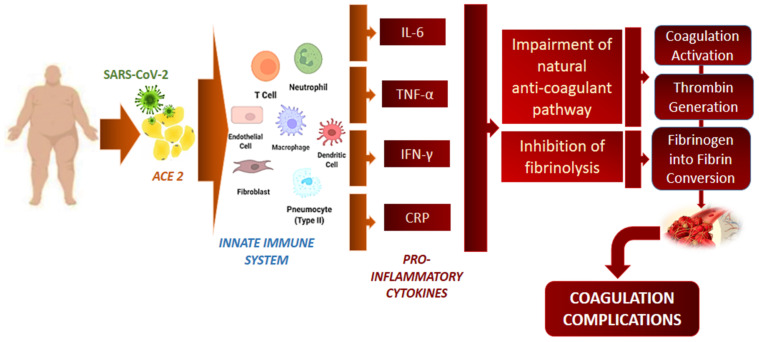
Figure 2.
The relation between SARS-CoV-2 infection and coagulation complications. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 stimulates the innate immune system by releasing proinflammatory cytokines. Interleukin (Il)-6, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interferon (IFN)-γ and C-reactive protein (CRP) interfere with the anticoagulant pathway and inhibit fibrinolysis. Due to all these mechanisms, coagulation is stimulated and ends with fibrin development.