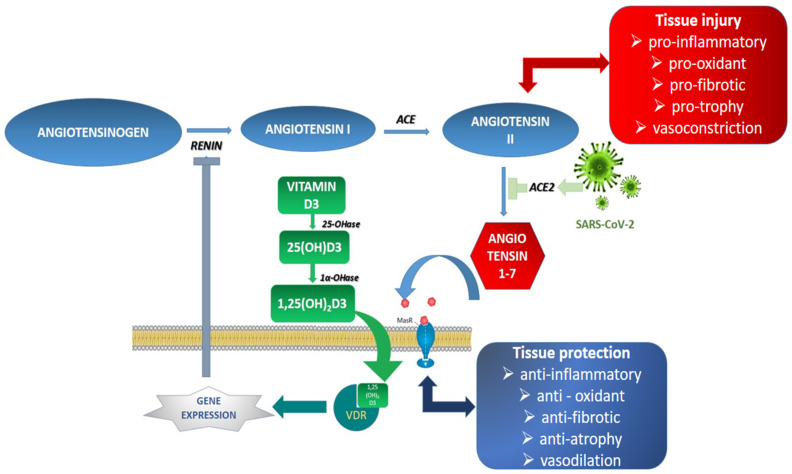
Figure 3.
Renin–angiotensin system: SARS-CoV-2 infection and implication of vitamin D. In SARS-CoV-2 infection, virus attachment to the ACE2 receptors blocks angiotensin II conversion into angiotensin 1,7 and leads to tissue injury reactions. Vitamin D function cascade [vitamin D3 is produced in the skin under ultraviolet radiation exposure, 25(OH)D3—25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcifediol, ergocalciferol), 1,25[OH]2D3—1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D (calcitriol)] and vitamin D receptor (VDR) are implicated in the suppression of the renin gene expression, thereby inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. Renin catalyses the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is further converted to angiotensin II. Normally, angiotensin II turns into angiotensin 1–7—the tissue protector via MasR receptors.