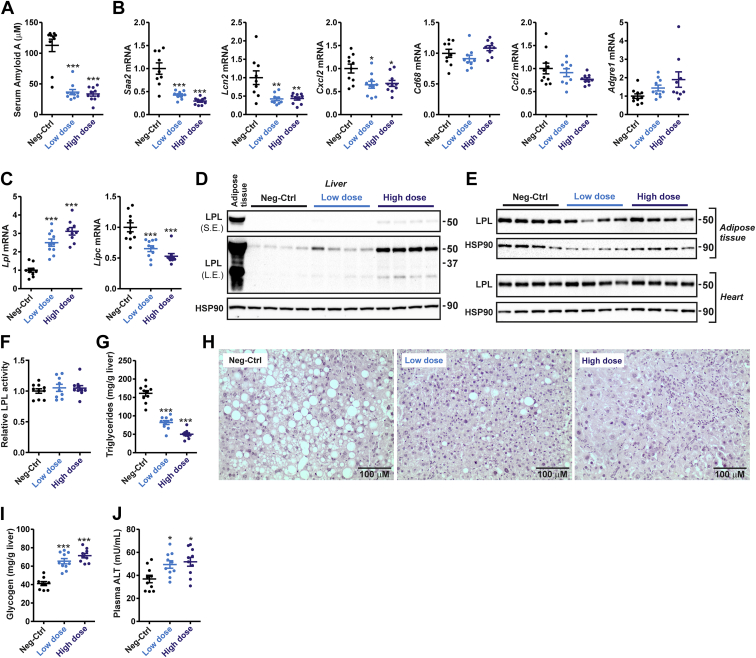
Figure 7.
ANGPTL4 ASO reduces steatosis and increases liver LPL content in diet-induced obese mice. Male C57BL/6J mice fed a HFD (45 en% fat) were randomly assigned to either treatment with Neg-Ctrl ASO (1.25 mg/kg, n = 10), low-dose ANGPTL4 ASO (0.625 mg/kg, n = 10), or high-dose ANGPTL4 ASO (1.25 mg/kg, n = 10) via subcutaneous injections twice a week for a total duration of 20 weeks. A: Serum amyloid A level in plasma. B: Hepatic mRNA levels of inflammatory markers as determined by quantitative PCR (qPCR). C: Hepatic mRNA levels of Lpl and Lipc. D: Hepatic LPL protein levels as determined by Western blot. Adipose tissue was used as a reference. HSP90 was used as a loading control. E: LPL protein levels in the adipose tissue and heart as determined by Western blot. HSP90 was used as a loading control. F: Adipose tissue LPL activity using EnzChek lipase substrate. G: Liver TG levels. H: Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of the liver. I: Liver glycogen levels. J: Plasma alanine aminotransferase activity. In the graphs, the horizontal bar represents the mean and the error bars represent SEM. Asterisk indicates significantly different from Neg-Ctrl ASO according to Tukey’s post hoc test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. HSP90, heat shock protein 90.