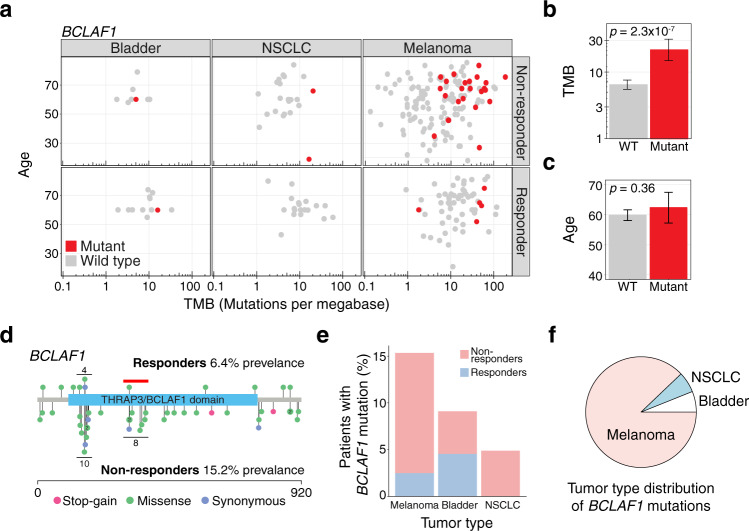
Fig. 3. BCLAF1 mutations identify a subset of non-responders with high tumor mutational burden (TMB).
a Age, TMB and tumor type for responders and non-responders with (red) and without (gray) BCLAF1 mutations. b TMB of patients with (n = 33) and without (n = 239) mutations in BCLAF1. Significance was calculated using a two-sided Welch’s t test and error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. c Age of patients with (n = 33) and without (n = 239) mutations in BCLAF1. Significance was calculated using a two-sided Welch’s t test and error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. d Protein location of mutations in BCLAF1 in responders (top) and non-responders (bottom). Mutations are color-coded by mutation type. Horizontal black lines indicate mutational clusters. The red horizontal line indicates a mutational cluster not present in responders. e Prevalence of BCLAF1 mutations in melanoma, bladder, and NSCLC cancer by ICB response status. f Distribution of BCLAF1 mutations by tumor type.