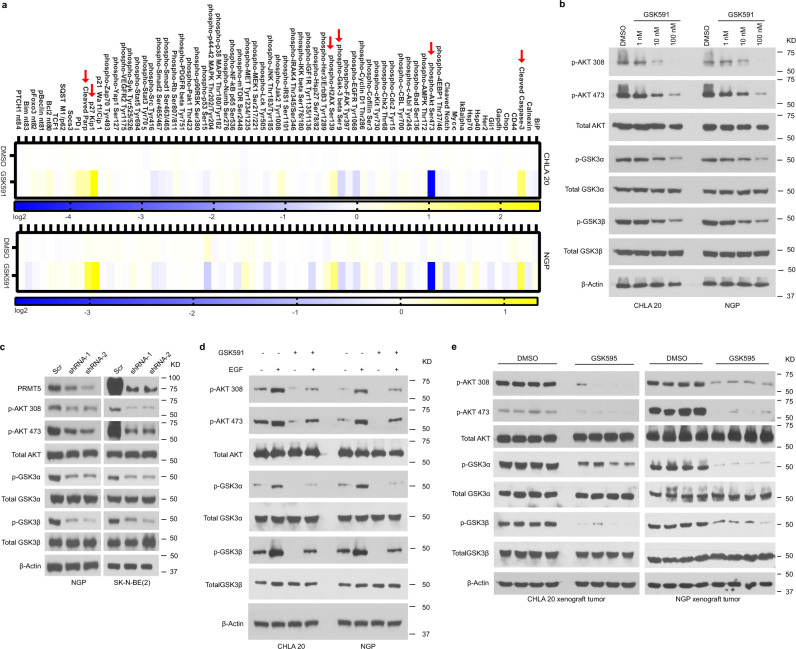
Fig. 3. PRMT5 inhibition impairs AKT signaling.
a Proteomics-based pathway screening by IPAD platform (immuno-paired-antibody detection assay) for the expression or modification of key proteins involved in more than 20 signaling pathways. Signals were normalized to internal levels of GAPDH and beta Tubulin. Heatmap showed differences between DMSO and GSK591 groups based on the average value from two independent experiments (n = 2 biologically independent samples). The color scale represented log2 fold changes over DMSO treatment. b Immunoblots showing phosphorylation of AKT, and its downstream targets phospho-GSK3α and phospho-GSK3β in CHLA20 and NGP cells treated with DMSO or increasing doses of GSK591. c Western blots of AKT phosphorylation and AKT downstream targets phospho-GSK3α and phospho-GSK3β in the presence and absence of PRMT5 in NGP or BE2 cells harboring scramble or shPRMT5. d Levels of phosphorylated AKT, GSK3α, and GSK3β with or without EGF stimulation in DMSO and GSK591-treated CHLA20 and NGP cells. e Activated AKT and its targets phospho-GSK3α and phospho-GSK3β were detected by Western blotting in xenograft tumors from vehicle or GSK595-treated mice. b–d Representative results from three independent experiments. Uncropped immunoblots are provided in the Source Data file.