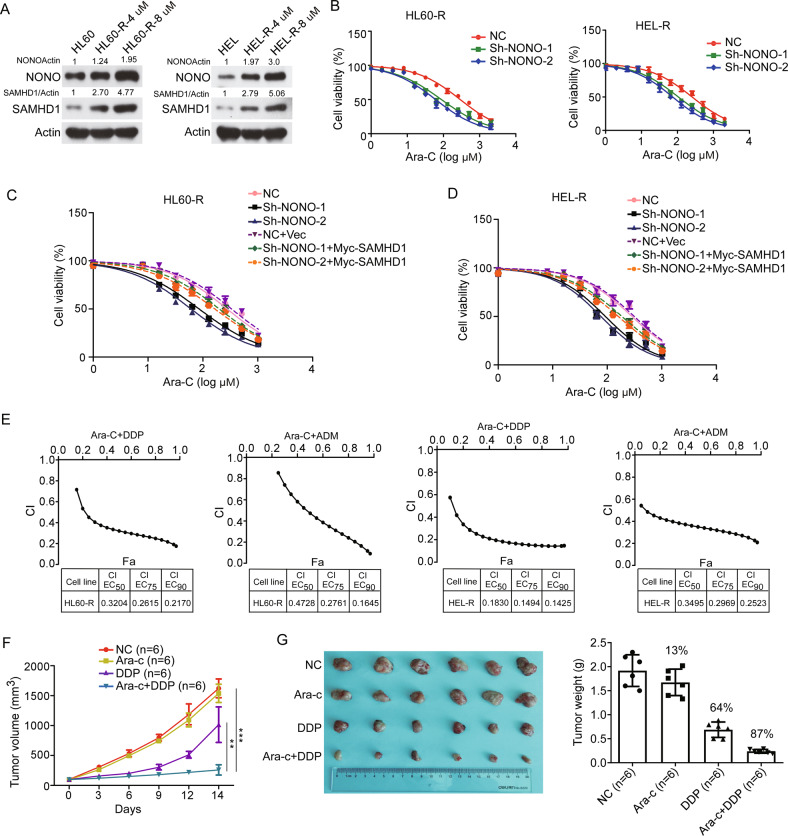
Fig. 7. NONO is crucial for the resistance of AML cells to Ara-C.
A Both NONO and SAMHD1 were upregulated in AML-resistant cells compared with the corresponding parental cells. The protein levels of NONO and SAMHD1 in HL60-R and HEL-R cells and the corresponding parental cells were evaluated by western blotting (P indicates parental cells. HL60-R-4 μM and HL60-R-8 μM, HEL-R-4 μM, and HEL-R-8 μM indicate the maximum sustained concentrations of Ara-C used for culture of the resistant AML cell lines). B Silencing NONO restored the sensitivity of resistant AML cells to Ara-C. Resistant AML cells with or without stable NONO silencing were treated with Ara-C at a series of concentrations as indicated for 48 h, and cell viability was evaluated by a CCK-8 assay (n = 3, mean ± SD). C, D HL60-R (C) and HEL-R (D) cells with or without stably silencing NONO were transfected with SAMHD1 or Vector for 24 h. Then the cells were treated with Ara-C at the indicated concentrations for 48 h, and cell viability was evaluated by CCK-8 assay (n = 3, mean ± SD). E DDP and ADM sensitized resistant AML cells to Ara-C. Plots of the CIs for Ara-C and DDP or ADM in HL60-R and HEL-R cells, as determined using the Chou–Talalay method (n = 3). F NOD/SCID mice bearing HL60-R cell xenografts were treated with PBS, Ara-C, DDP, or a combination of Ara-C and DDP, and tumor growth was monitored. n = 6 for each group. G The tumor weights for each group as indicated in Fig. 7F. In B-D, 2-way ANOVA was used to compare the behavior of the cells treated as indicated and negative control cells. F, G, a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). For respective immunoblots, the protein levels were quantified by ImageJ software.