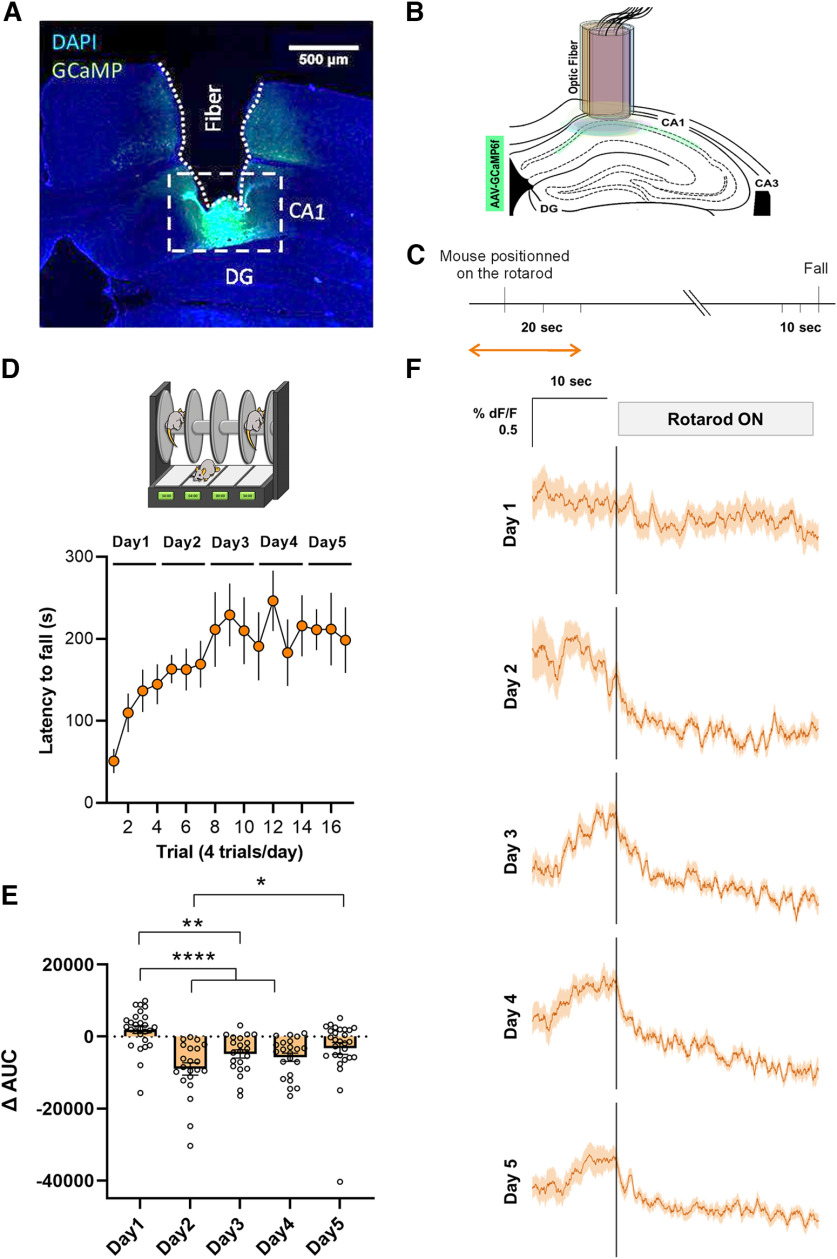
Figure 2.
Accelerating rotarod task induced-functional plasticity in the hippocampal CA1 neurons. A, Representative viral expression of AAV-GCaMP6f and (B) placement of the fiber-optic probe in CA1 for each mouse depicted in different colors accordingly. DG, dentate gyrus. C, Experimental design of fiber photometry. Analysis was performed during the time windows indicated by the orange arrow. D, Mice implanted with the fiber-optic probe were subjected to the accelerating rotarod task. E, Quantification of the change in the AUC between [−10, 0 s] and [0, 10 s] relative to the placement of the animal in the rotarod. F, Averaged traces of GCaMP6f signal expressed as ΔF/F% for 10 s before and 20 s after the mouse was placed on the rotarod. All the trials (n = 7 mice) were averaged on each training sessions (days 1–5).