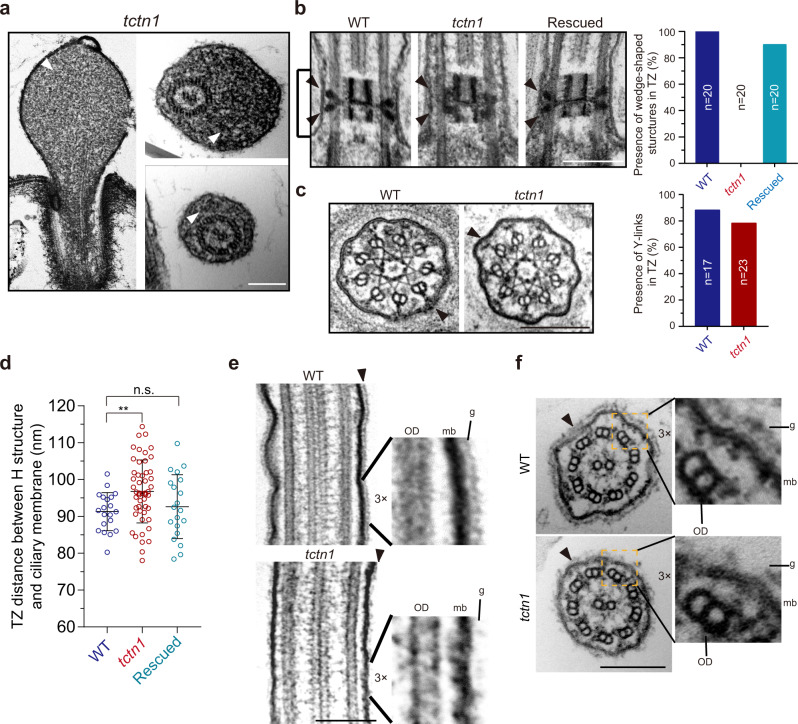
Fig. 2. Loss of TCTN1 causes ultrastructural defects of the ciliary membrane and the TZ.
a EM images showing ciliary bulges with electron-dense material (white arrowheads) in a portion of tctn1 cells. Scale bar, 200 nm. b, c Longitudinal sections (b) and cross sections (c) through the TZ (b, brackets) of WT, tctn1 and rescued cells. The wedge-shaped structures (b, black arrowheads) and Y-links (c, black arrowheads) were indicated. Quantification of the presence of wedge-shaped structures in the longitudinal section (n = 20, number of wedge-shaped structures) and Y-links in the cross section (n = 17 for WT, n = 23 for tctn1, number represents the thin sections counted.). The presence of at least one Y-link in the thin section is considered as normal. Scale bar, 200 nm. d Scatter plot depicting the distances between the “H” structure and the ciliary membrane in WT, tctn1, and rescued cells. Data are the mean ± SD (n = 20). Statistical significance was determined with an unpaired t test. n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01 by two tailed. e, f TEM images of longitudinal (e) and cross (f) sections of the cilia from WT and tctn1 cells. Glycocalyx on the surface of ciliary membrane was indicated with black arrowheads. The high magnification regions were indicated by dotted boxes. OD outer doublet microtubule, mb ciliary membrane, g glycocalyx. Scale bar, 200 nm. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.