Figure 3. Mechanism for the anti-fibrotic activity of SCGB3A2.
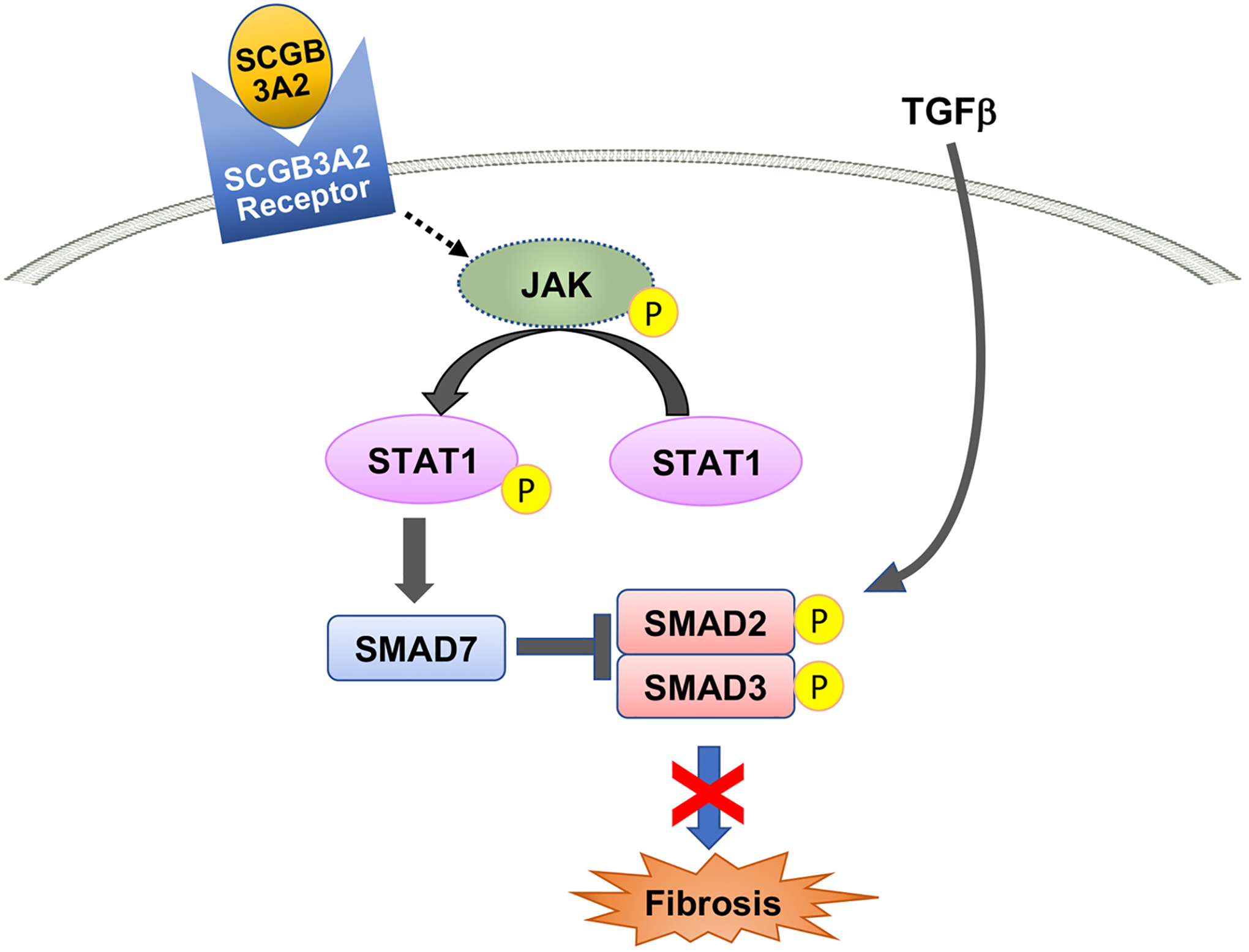
SCGB3A2 anti-fibrotic signaling starts upon binding of SCGB3A2 to a SCGB3A2 receptor, which activates STAT1 phosphorylation, increases SMAD7, and suppresses SMAD2/3 phosphorylation, resulting in the suppression of expression of genes involved in fibrosis such as collagens, leading to inhibition of fibrosis.
