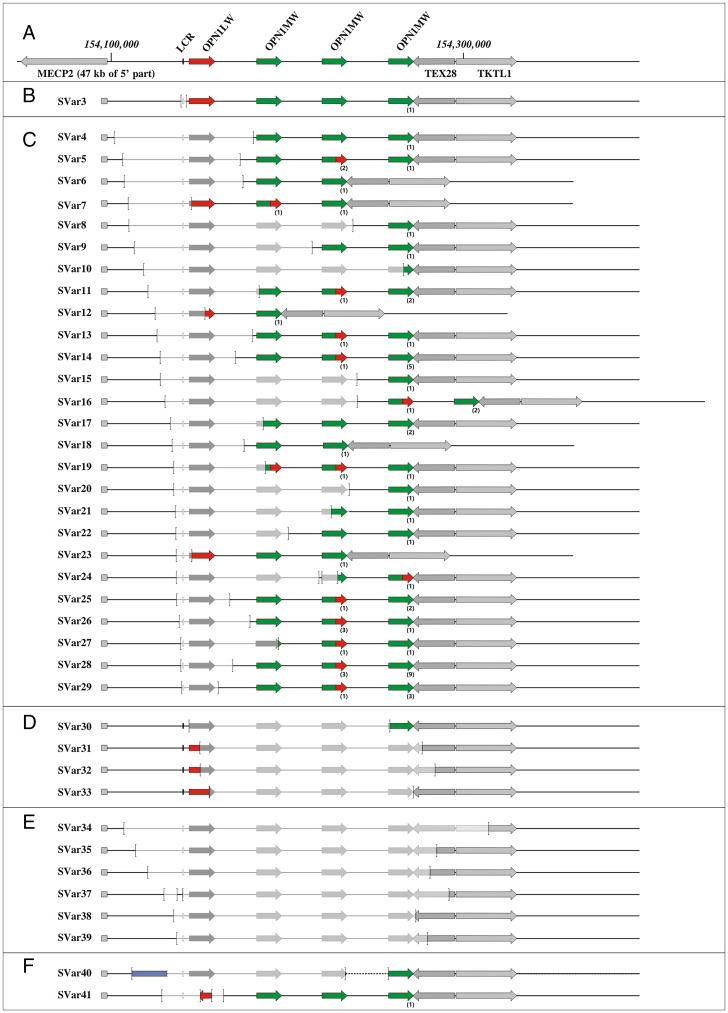
Fig. 2.
Structure, extent, and composition of BCM-linked SVs observed in this study. (A) Map of the OPN1LW/OPN1MW gene array with a single OPN1LW and three downstream OPN1MW gene copies (according to the GRCh38/hg38 genome assembly). The OPN1LW and OPN1MW gene(s) are depicted by red and green arrows, respectively. The LCR is shown as a rectangle upstream of the OPN1LW gene. Flanking genes (MECP2, TEX28, and TKTL1) are shown by gray arrows. (B–F) Categories of BCM-linked SVs including deletions restricted to the LCR (B), SVs covering the LCR and parts of the OPN1LW/OPN1MW gene cluster (C), SVs covering OPN1LW/OPN1MW gene cluster but intact LCR (D), deletions of the OPN1LW/OPN1MW gene cluster (including the LCR) and extending into the downstream TEX28 and TEKTL1 genes (E), and complex structural rearrangements (F). The SV breakpoints are marked by brackets and deleted parts are indicated by lighter gray color. The presence of OPN1MW•OPN1LW hybrid genes is indicated by arrows half-colored in green and red. The blue box in SVar40 represents an interstitial insertion of chromosome 20 sequences. Additional copies of OPN1MW or OPN1MW•OPN1LW hybrid genes are indicated by the number in parentheses below the arrows. Note that the structure of SVar1, SVar2, and SVar42, which cannot be properly displayed at this scale, is displayed in SI Appendix, Figs. S5, S8, and S2, respectively.