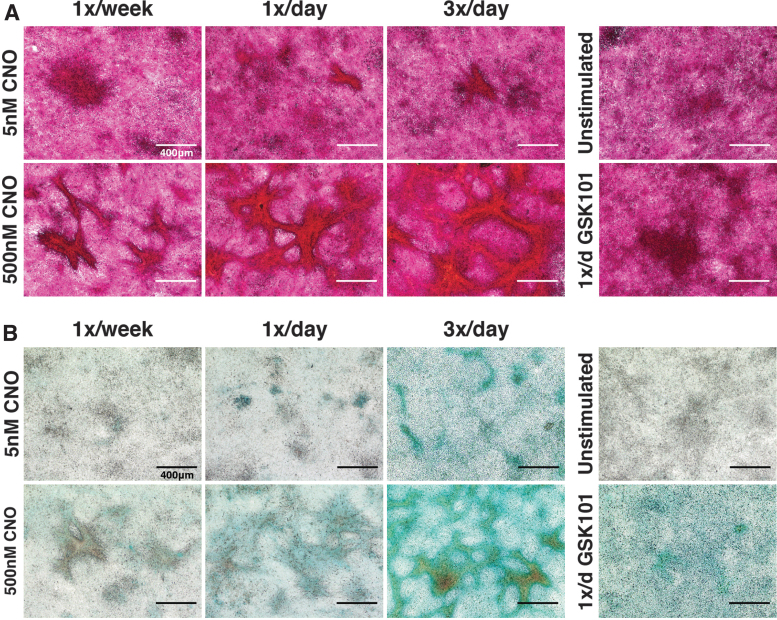
FIG. 4.
CNO stimulation of hM3Dq-ATDC5 cells drove concentration- and frequency-dependent neotissue formation. (A) PR staining demonstrated deep and robust staining for collagens within cell condensations/nodules formed following 2 weeks of CNO stimulatory culture. The size and alignment of tissue nodules increased with CNO concentration and dosing frequency; PR staining of nodules changed from a purple/deep red under lower CNO stimulation regimes to bright red-orange with increased stimulation pressure (reflecting increased collagen content), whereas inter-territorial cells stained light pink/light purple (indicating little to no collagen deposition). Purple/deep red stained cell clumps were observed in GSK101-treated and unstimulated micromass cultures; however, these cells did not exhibit the tissue alignment and condensations observed in the CNO-treated cultures. (B) Similar outcomes were observed for AB staining of proteoglycans; CNO induced concentration- and frequency-dependent enhancements in proteoglycan deposition (blue). GSK101-stimulated cultures developed appreciable AB staining, though this was more diffuse compared with CNO cultures, whereas unstimulated cultures were relatively devoid of AB staining. AB, alcian blue; PR, picrosirius red.