Fig. 6.
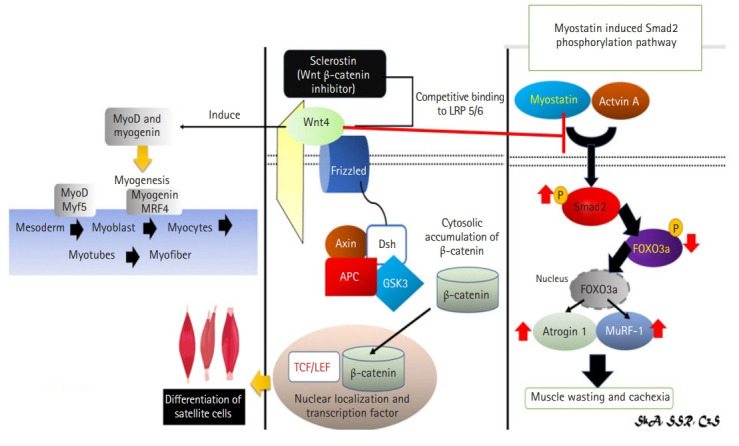
Mechanism of sclerostin as inhibitor of Wnt4 signaling in muscle via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and Wnt4’s effect to myostatin.4,29,41,42,44,45) (Left and center) Wnt4 bone and muscle crosstalk occurs via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which inhibit by sclerostin. Wnt4 overexpression increased Myf5 expression, which is necessary for myogenesis. (Right) Myostatin is also thought to be involved in the Wnt4 pathway. Wnt4 induces myogenesis by inhibiting myostatin thus preventing muscle wasting and cachexia. Myf5, myogenic factor 5; LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; Dsh, disheveled; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor.
