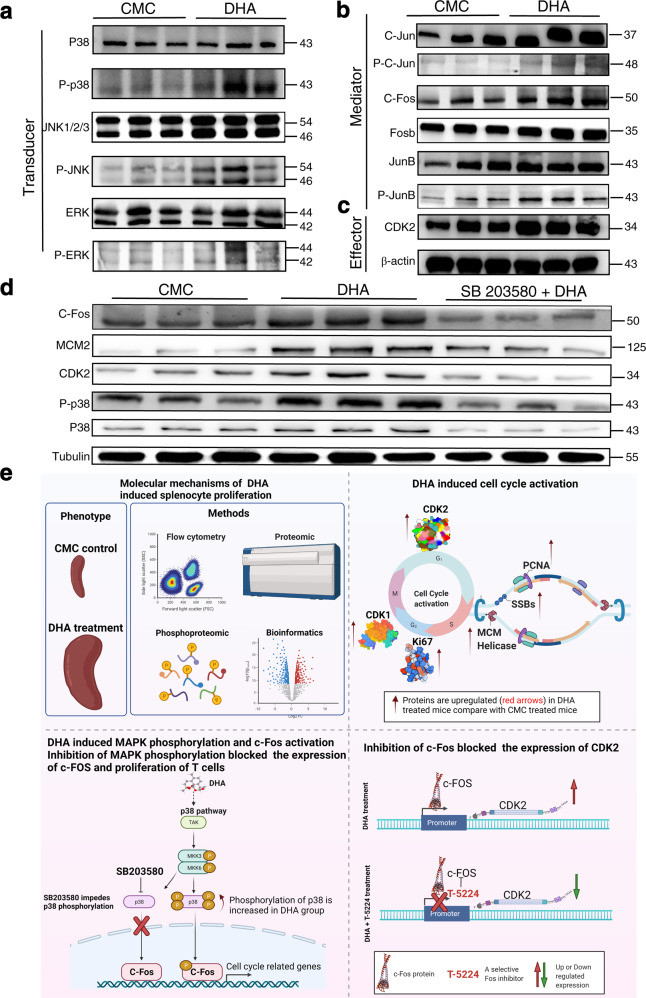
Fig. 5.
DHA regulated cell-cycle via the p38/JNK MAPK pathways. a–c Representative images of Western blot (WB) of phosphorylated MAPK proteins, AP-1 proteins, and CDK2. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Molecular weight (kDa) was labeled at the right. d The expression and phosphorylation of p38 and JNK from DHA-treated alone, the group with inhibitor and the control group were examined with specific antibodies. The expression of CDK2, MCM2, and c-Fos from both DHA-treated alone, the group with inhibitor and the control group were examined with specific antibodies. The effect of DHA was significantly inhibited by SB203580, a specific inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38), which downregulated the expression of c-Fos, MCM2, and CDK2. e Proposed mechanism of DHA-mediated regulation on p38 MAPK pathway and c-Fos complex. DHA induced an enlargement of the spleen and selectively promoted the proliferation of subgroups of splenic T cells. Importantly, DHA upregulated the expression of cell proliferation-associated proteins including CDK1, CDK2, Ssb, PCNA, MCMs, by promoting the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the activation of c-Fos in the spleen. Inhibition of p38 MAPK and c-Fos blocked T cell proliferation. This figure was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com/). Agreement number is WJ23R5400C. DHA=dihydroartemisinin group, CMC=CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) solvent solution control group. N = 3 (with biological triplicates) in the WB quantitation. p-p38, phosphorylated-p38 MAPK; p38, total p38 MAPK; SB203580 is a specific inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38); T-5224 is a specific inhibitor of C-Fos