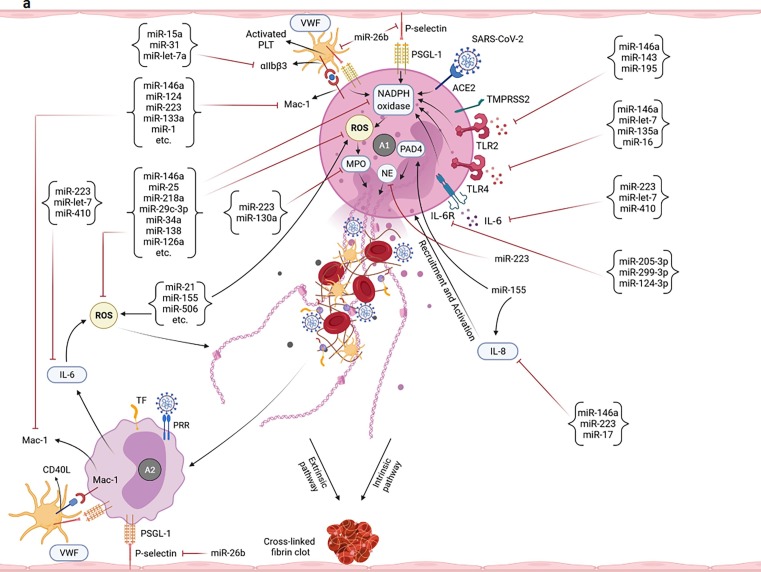
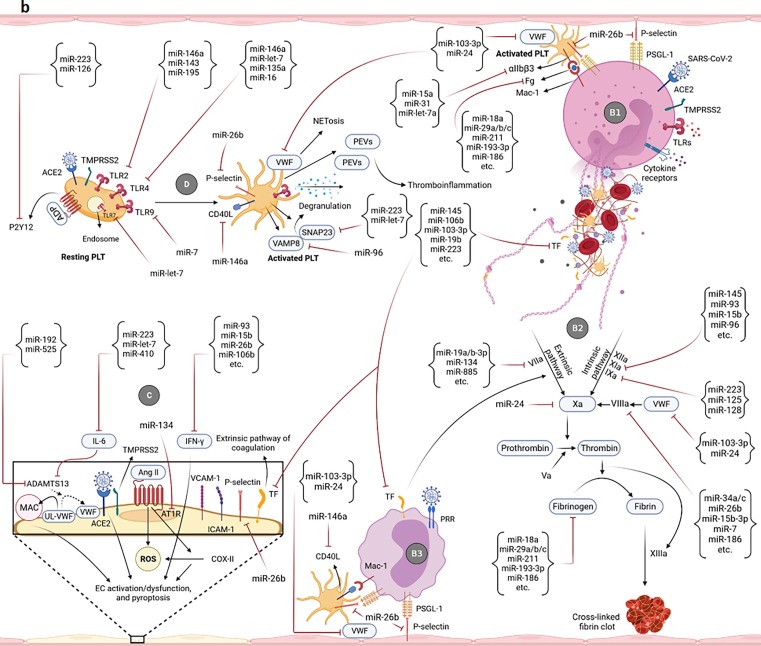
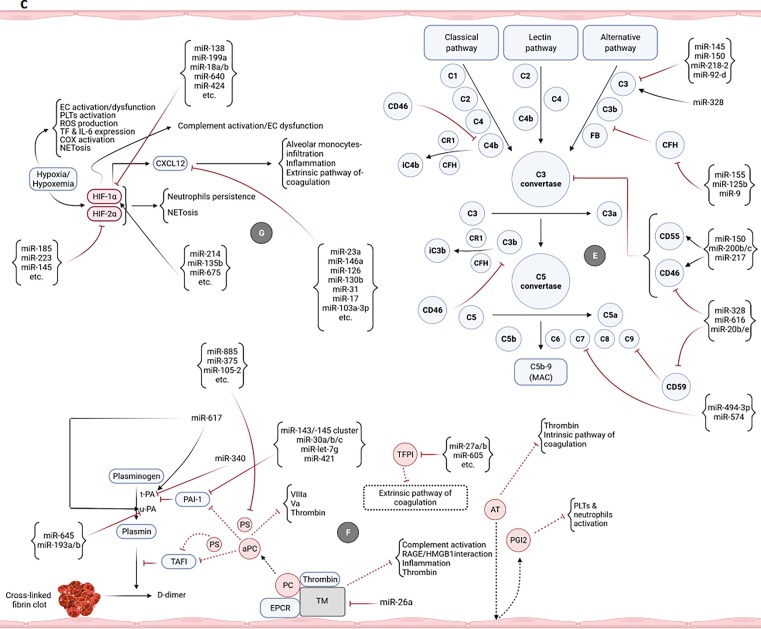
Fig. 2.
Potential of miRNAs in targeting/regulation of key molecules involved in the development of uncontrolled immunothrombosis. a-A1) According to the research evidence, many miRNAs can target IL-8, ROS, and different receptors as well as enzymes participating in the NETosis process. Adhesion molecules-mediated neutrophils-PLTs and neutrophils-ECs interactions can also be affected by miRNAs. Some of these small RNAs also cause the production of ROS and induction of NETosis. The modulation of the NETosis process by miRNAs can indirectly affect some of the adverse outcomes resulting from their excessive production such as activation of monocytes, coagulation pathways, etc. a-A2) miRNAs can affect the interactions of monocytes with PLTs as well as ECs and control the immunothrombosis. The modulation of monocytes-released pro-inflammatory cytokines by miRNAs can also restrict the NETs formation. b-B1) Multiple miRNAs target the key molecules simultaneously involved in both NETosis and coagulation processes such as VWF, TF, Fg, and αIIbβ3. b-B2) miRNAs can also regulate the expression levels of molecules/factors with the key roles in extrinsic, intrinsic, and common pathways of coagulation leading to more control of thromboinflammation. b-B3) The PLTs-/ECs-monocytes interactions and TF on the surface of monocytes are targeted by miRNAs leading to the regulation of the coagulation cascade and immunothrombosis. b-C) Several miRNAs can affect the expression of molecules involved in the ECs activation/dysfunction and pyroptosis. Causing the ECs damage, ADAMTS13 is also targeted by some of these small RNAs. Targeting the TF on the ECs is followed by the limitation of the extrinsic coagulation pathway. b-D) The expression regulation of different receptors of PLTs with central roles in their activation is accomplished by miRNAs. Targeting some other molecules such as CD40L, VWF, P-selectin, SNAP23, and VAMP8 can also affect the activation and degranulation of PLTs leading to more restriction of uncontrolled immunothrombosis. c-E) Several miRNAs can target the complement factors and regulators. They negatively or positively regulate their expressions and affect the uncontrolled immunothrombosis. c-F) The negative and positive regulations of molecules involved in the fibrinolysis process are done by some miRNAs leading to the limitation of fibrin deposition and development of the uncontrolled immunothrombosis c-G) The expressions of hypoxia/hypoxemia-induced HIF-1α and HIF-2α are affected by several miRNAs. CXCL12 is also considered a target molecule of miRNAs affecting the uncontrolled immunothrombosis.