Fig 2. Generation and testing of MNA integrating hapten and NK1R antagonists.
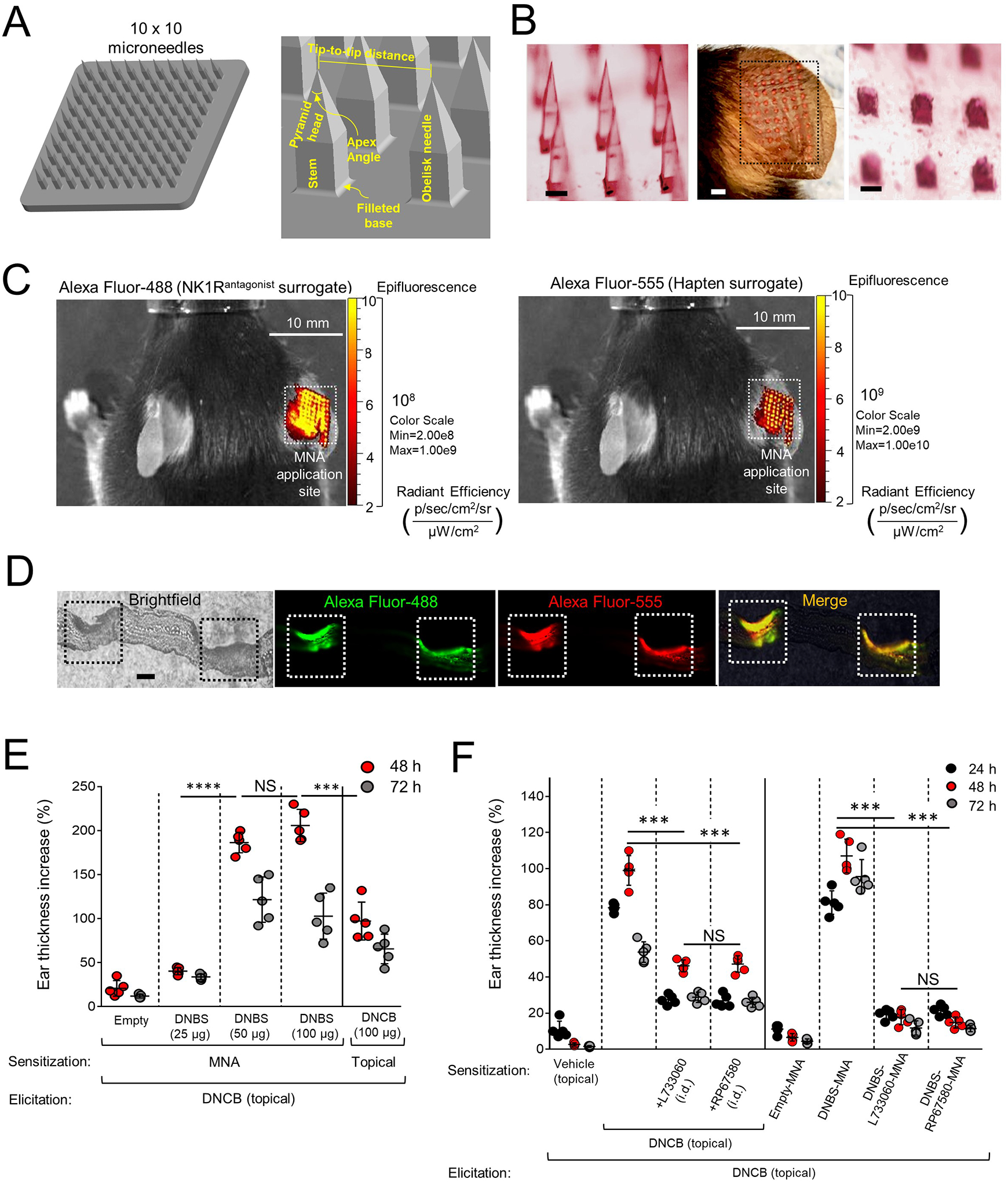
A) Three-dimensional design of MNA and geometric parameters. B) Stereomicroscopy images of the microneedles before (left) and after (right) application to mouse ears. Scale bars, 200μm. Center, MNA-delivered cargo traces (dotted line square) on the mouse ear. Scale bar, 1mm. C) Live-animal fluorescence images of a mouse treated with MNA on the ear skin, showing delivery of Alexa Fluor-488 (left) and Alexa Fluor-555 (right). D) Cryosection of a mouse ear skin showing (left) two areas of MNA penetration (squares), and the corresponding images by fluorescence microscopy showing delivery of Alexa Fluor-488 (green) and Alexa Fluor-555 (red) to skin layers. Scale bar, 40μm X100. E) CHS induced by sensitization with MNA loaded with DNBS versus DNCB applied topically. Each dot represents one mouse. F) Comparative CHS in mice sensitized with topical DNCB plus NK1R antagonists injected i.d. or with DNBS-NK1Rantagonists-MNA. In (E) and (F), a representative experiment of 3 is shown, 5 mice per group. Means ± SD analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, NS: not significant. Statistic comparisons among values obtained 48 h following ear skin elicitation.
