Fig 3. DNBS and NK1R antagonists integrated in MNA restrain hapten-induced inflammation in mouse and human skin.
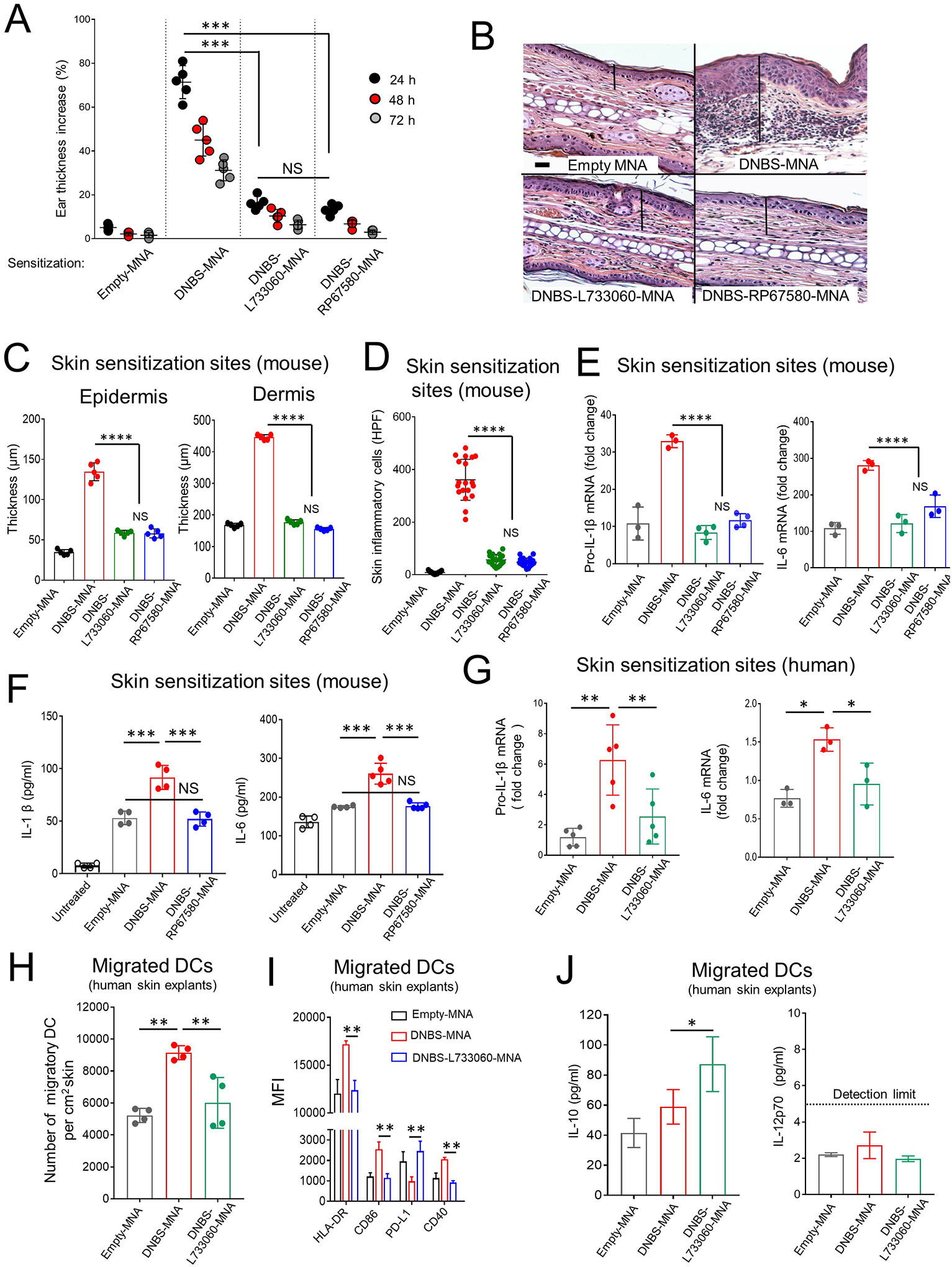
A) Inflammation in WT B6 mice (by the ear thickness) after MNA sensitization. One experiment of 5. Five mice per group. B) Microscopic images of the ears of mice in (A) showing epidermal-dermal thickness (lines) and leukocyte infiltrate. H&E, X200, scale bars 20μm. C) Epidermal and dermal thickness of mouse ears in (A). Five mice / experimental group. D) Quantification of inflammatory cells in the skin sections of mice in (A). Means±1SD of 20 microscopic high-power fields (HPF, X40) per skin section. A representative experiment of 3. Five mice per group. E) Content of IL-1β and IL-6 transcripts in the ears of mice. F) Content of IL-1β and IL-6 in the ears of mice. In (E) and (F) One experiment of 3. G) IL-1β and IL-6 transcripts in human skin treated with MNAs. Each dot represents a skin sample from a different donor. A representative experiment of 3. H) Quantification of DC migrated from the skin samples in (G). One experiment of 3. I) Expression of HLA-DR, CD86, PD-L1 and CD40 on DC mobilized from the human skin shown in (G). J) Concentration of IL-10 and IL-12p70 in supernatants of the migratory DC in (G). Means ± 1 SD analyzed by 1-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman Keuls test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001, NS: not significant.
