Fig 4. Skin CHS requires NK1R signaling in keratinocytes and DC.
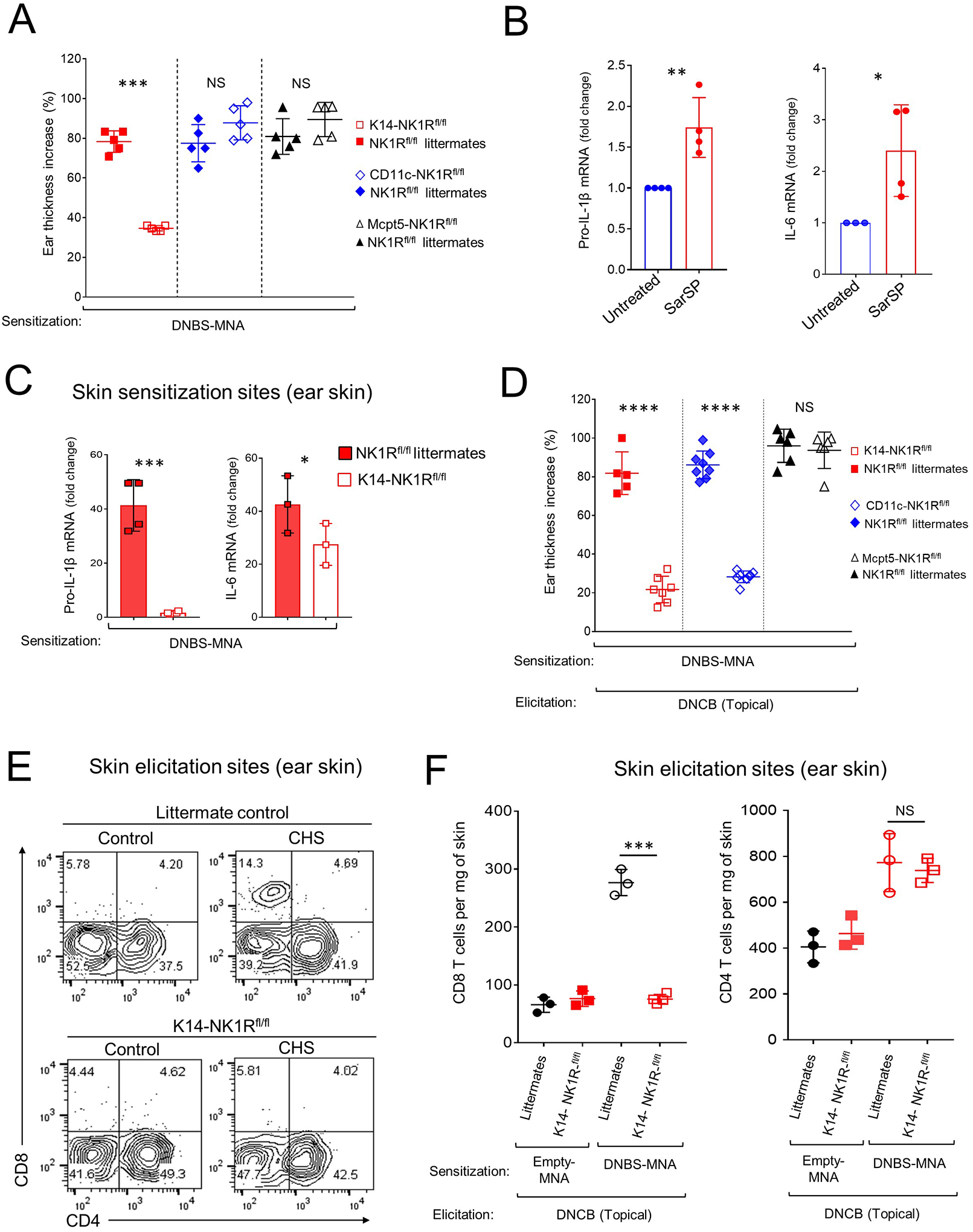
A) Inflammatory response, by ear thickness increase, in K14-NK1Rfl/fl, CD11c-NK1Rfl/fl, or Mcpt5-NK1Rfl/fl and littermate controls. One experiment of 3. Five mice per experimental group. B) IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA in COCA cells cultured alone or with SarSP. C) IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA content in the ears of K14-NK1Rfl/fl mice and littermate controls treated with DNBS-MNA. One experiment of 3. Four mice per experimental group. D) CHS effector response in K14-NK1Rfl/fl, CD11c-NK1Rfl/fl, and Mcpt5-NK1Rfl/fl mice treated with MNA. One experiment of 3. Five mice per group. E) Quantification of CD4 and CD8 T cells in the ears of K14-NK1Rfl/fl mice and littermate controls in (D) 48 h after elicitation. Numbers are percentages of cells per quadrant. F) Quantification of T cells in the ears of mice in (E). One experiment of 3. Means ± 1 SD analyzed by 1-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. NS: not significant. In (A) statistic comparisons among values obtained 24 h following ear skin elicitation are depicted. In (D) statistic comparisons among values obtained 48 h following ear skin elicitation are depicted.
