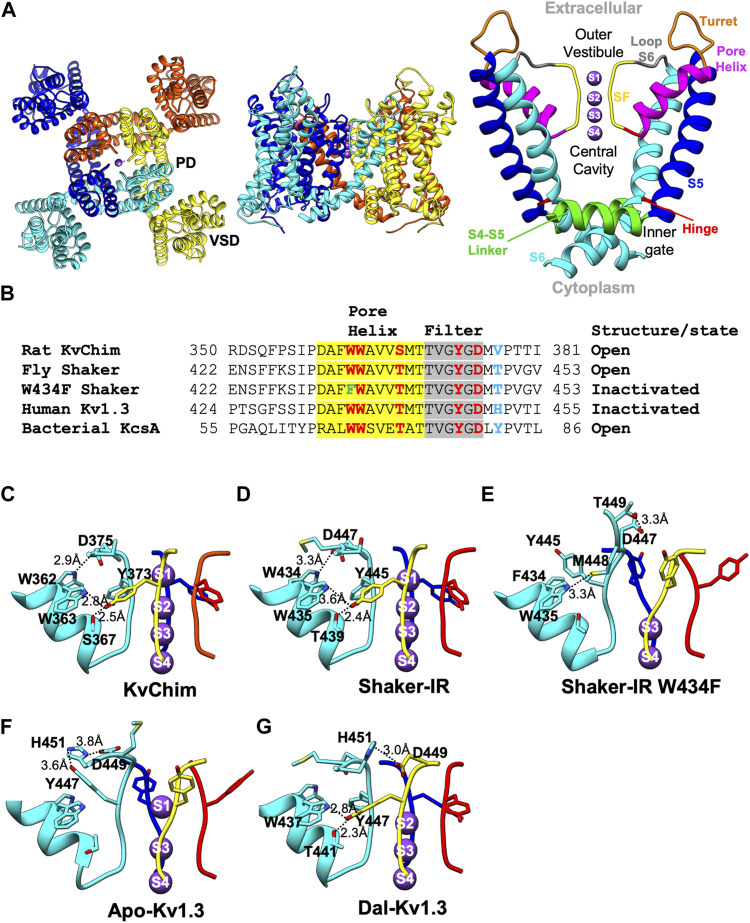
FIGURE 1.
Structures of Kv channels in open-conducting, C-type open-inactivated and peptide-bound conformations. (A) Structure of KvChim (PDB:2R9R) viewed from the extracellular (left) and membrane planes (middle). The pore domain (PD) shown on the right is formed by S5 and S6 helices together with a P-loop consisting of a turret, pore-helix, SF and loop-to-S6. In the channel’s pore, the inner gate, central cavity, SF, outer vestibule, hinge and S4-S5 linker are shown. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of P-loops of KvChim, Shaker-IR, Shaker-IRW434F, human Kv1.3 and bacterial KcsA. Residues involved in hydrogen bond networks are highlighted. (C–G) Hydrogen-bond networks in KvChim, PDB:2R9R; Shaker-IR, PDB:7SIP; Shaker-IR W434F, PDB:7SJ1; Apo-Kv1.3, PDB:7WF3, and Dal-Kv1.3, PDB:7WF4. Individual subunits are colored cyan, blue, red, and yellow. Selected residues are shown for clarity. Distances between hydrogen-bonded residues are shown. K+ (purple spheres) are shown at K+-binding sites, which are numbered.