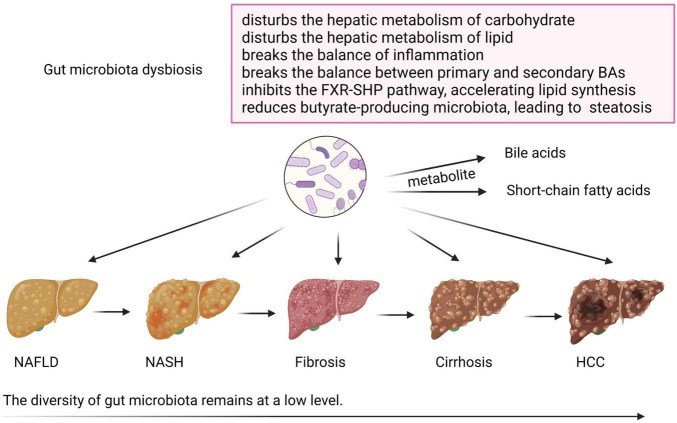
FIGURE 2.
The role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its advanced disease progression. During the progression of NAFLD, the diversity of gut microbiota remains at a low level. Gut microbiota dysbiosis disturbs the hepatic metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids and breaks the balance of inflammation. Disturbed gut microbiota also changes the normal metabolism of bile acids (BAs) and short-chain fatty acids, and may cause NAFLD via breaking the balance between primary and secondary BAs, inhibiting the FXR-SHP pathway, which accelerates lipid synthesis, and reducing butyrate-producing microbiota, which causes steatosis. Created with BioRender.com.