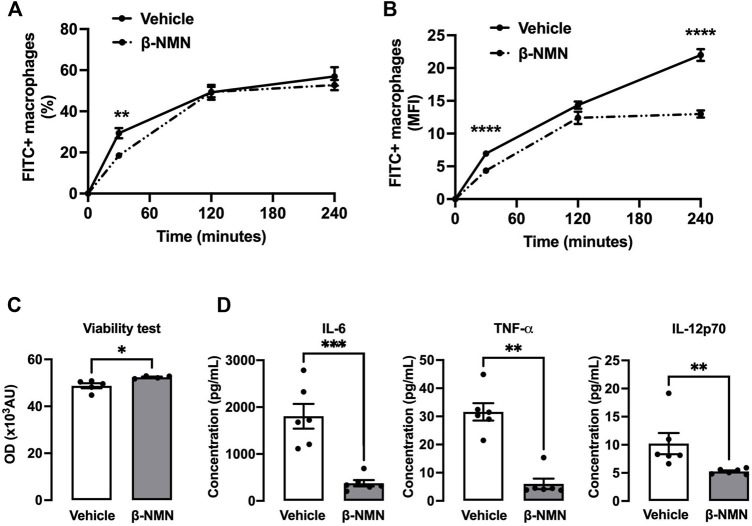
FIGURE 4.
Functional properties of peritoneal macrophages following stimulation with E. coli in the TGC-induced peritonitis mouse model. (A,B) Phagocytosis of peritoneal macrophages. Three days post TGC administration, macrophages from peritoneal lavage fluid were cultured on plates and stimulated with pH-Rhodo-labeled E. coli. The proportion of phagocytic macrophages at 30, 120, and 240 min was analyzed by flow cytometry. The quantity of engulfed E. coli was expressed as % of total macrophages (A) or as the mean of fluorescence intensity (MFI) (B). (C,D) Viability and pro-inflammatory secretion of peritoneal macrophages. Three days post TGC administration, macrophages were co-cultured with E. coli for 24 h. (C) Viability of macrophages was assessed by the AlamarBlue® assay and expressed as optical density (OD). (D) Secreted cytokine concentrations (IL-6, TNFα, and IL-12p70) were determined in the cell culture supernatant by flow cytometry using a bead-based immunoassay. IL = interleukin; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-alpha. All data are mean ± SEM; n = 4–6 for each group; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 vs. vehicle.